Are you trying to learn more about the animal body? Or are you trying to delve deep into the microscopic world of animal cells? Either way, you have landed on the right destination! Let’s think of animals beginning with N, say Nilgai.
The body of a Nilgai, the largest antelope in Asia, is built with millions of building blocks or cells. The kingdom of animal cells is a new, captivating world with intricate details.
Buckle up your seat belts as we are ready to dive into the journey of an animal cell.
What is an Animal Cell?
Our first step is to understand the definition of an animal cell. To be accurate, a cell is the basic structural and functional unit of an animal’s life. In scientific terms, it is also known as the primary building block of any living organism.
Like humans and plants, animal cells also differ in shape, size, and function. However, their characteristics remain similar irrespective of the species.
Moving forward, an animal cell is a semi-permeable plasma membrane that appears to enclose this building block. The membrane separates and protects the internal components from the harsh external atmosphere.
What components do you ask?
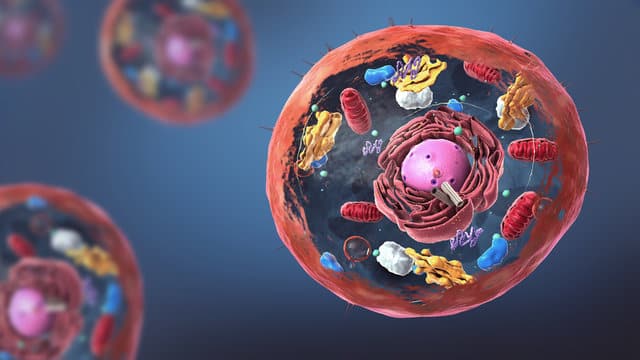
The internals of an animal cell are a new microscopic world like our galaxy. A variety of further microscopic organelles specialized functions to keep the cells alive.
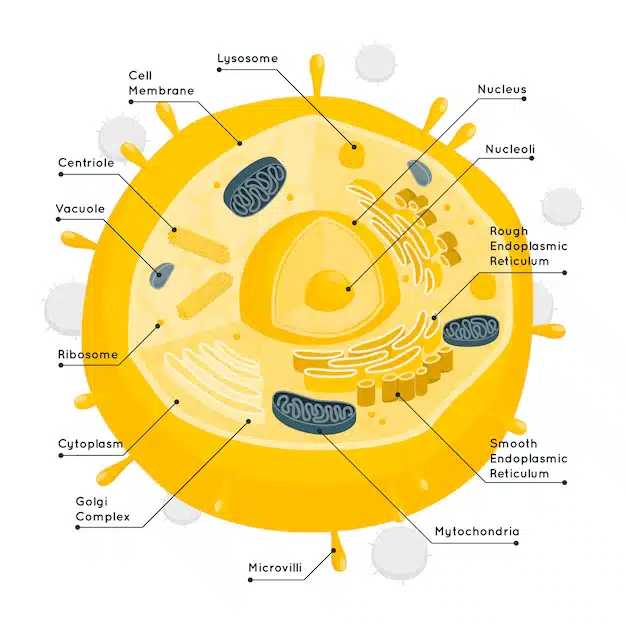
The nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes are major in-cell organelles with specific roles.
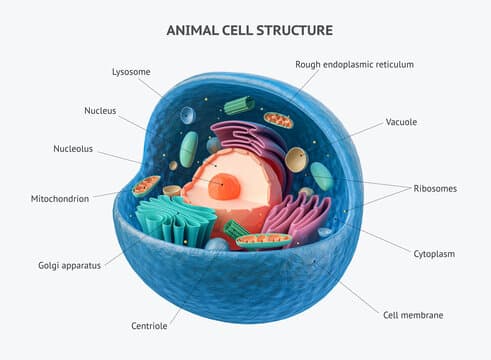
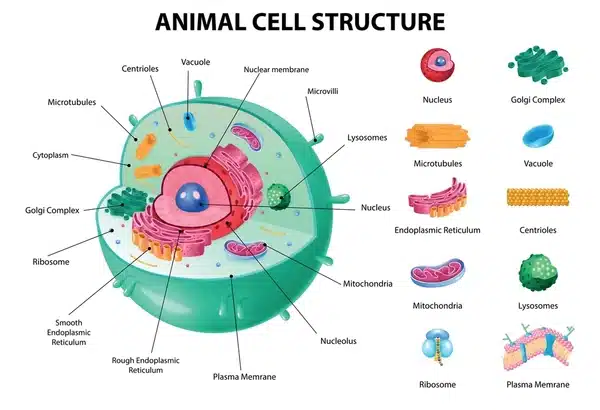
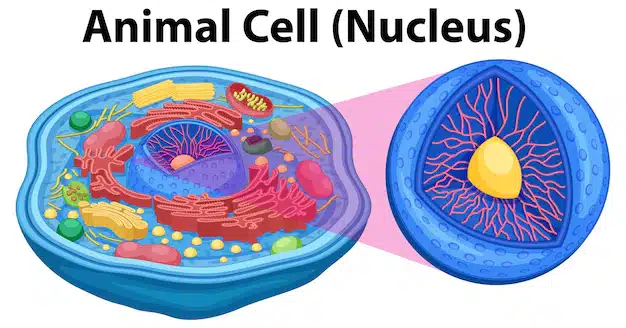
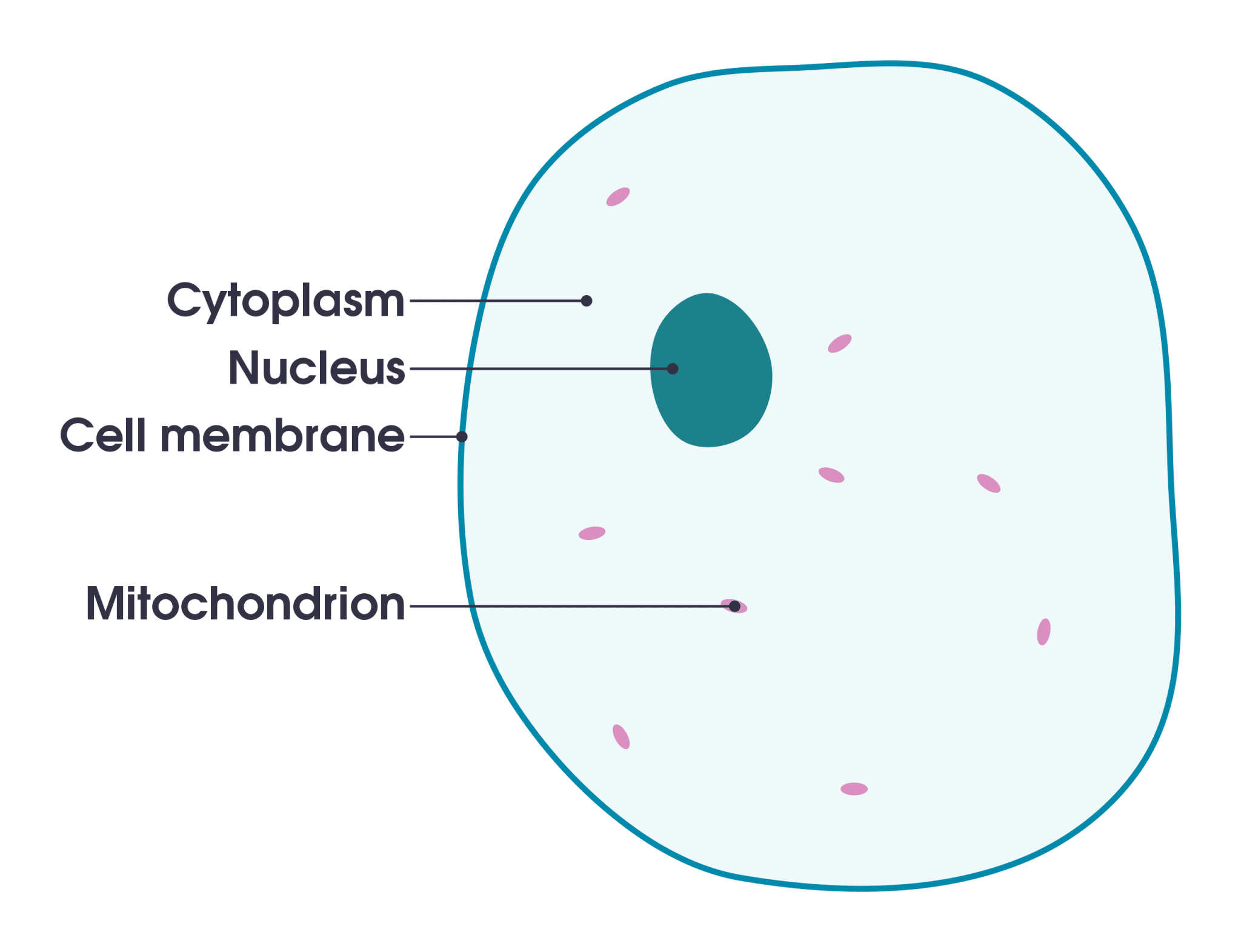
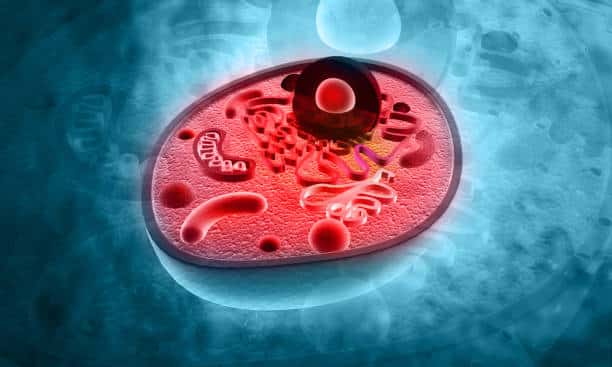
Pictorial Representation of An Animal Cell
If you are having difficulty imagining or understanding an animal cell’s organelles, we are here to help! The pictorial representation above will help you understand the components encapsulated within a cell.
Every intricate microorganism you see has specified roles to contribute. It takes teamwork to keep a cell alive and an animal healthy.
Understanding the Structure of Animal Cell
After closely examining the structure and components of an animal cell, it is time to understand their various functionalities.
It takes practical effort and a strong band of responsible microorganisms to keep cellular powerhouses up and running.
The outermost boundary of the cell is the plasma membrane that acts as a strict gatekeeper regulating traffic in and out of the cell.
However, that is just the beginning! Below is a list of the internal components that form a dynamic system within each animal cell.
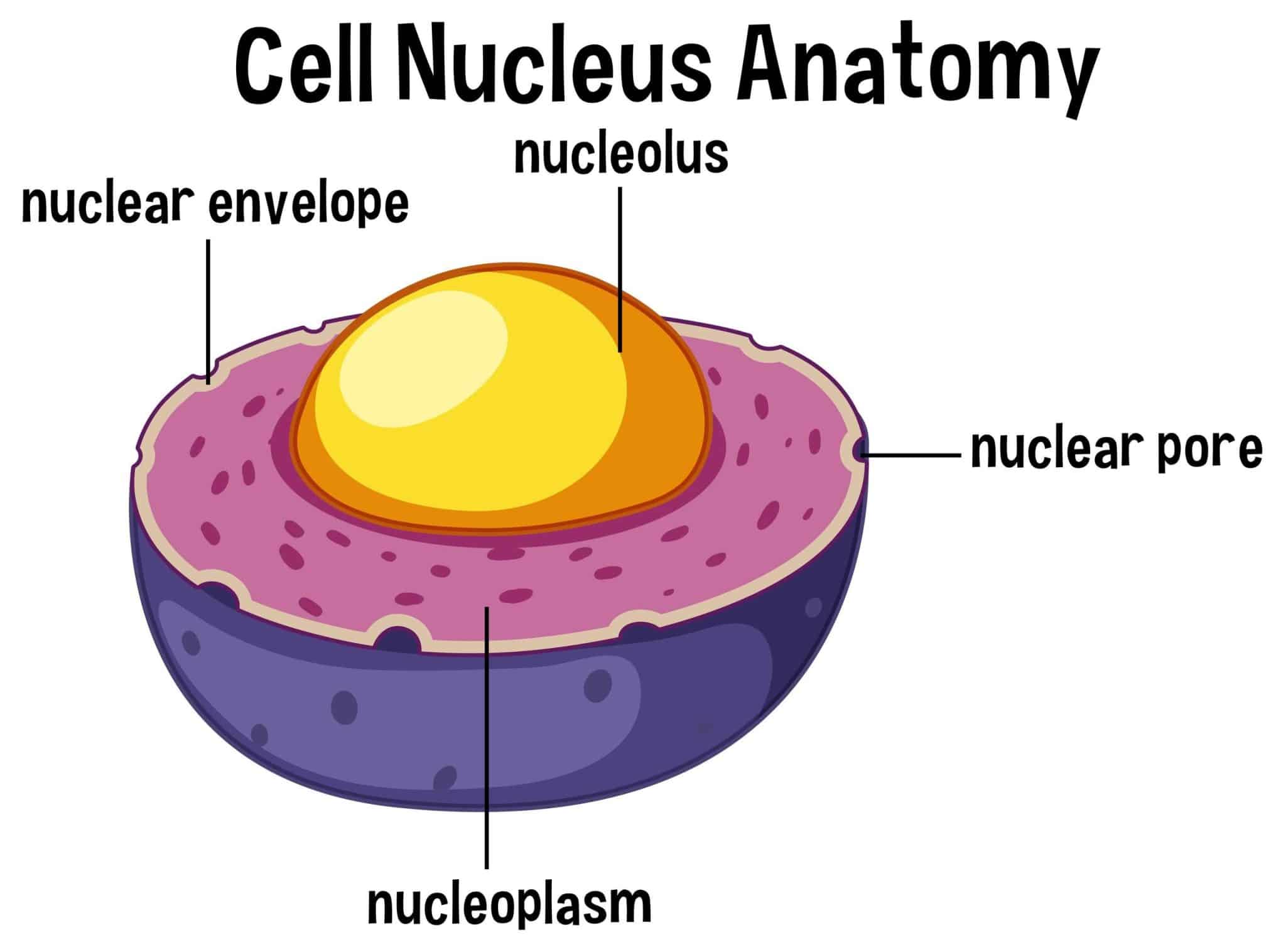
1. Nucleus
The nucleus within an animal cell is the primary command center. It houses the nucleolus nucleosome and genetic material or DNA to regulate all cellular activities.
A double membrane called the nuclear envelope further covers the nucleus to control DNA replication.
2. Nuclear Membrane
The nuclear membrane, or the nuclear envelope, is a double-layer membrane surrounding the nucleus.
It helps in separating the nuclear contents from the cytoplasm.
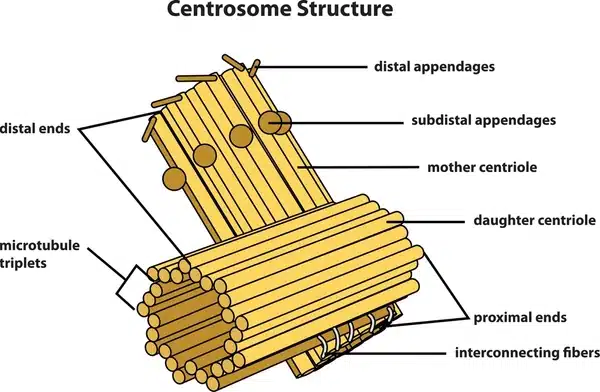
3. Centrosome
The centrosome located near the nucleus contains a pair of centrioles. It contributes to cell division by organizing microtubules that form the spindle apparatus during mitosis.
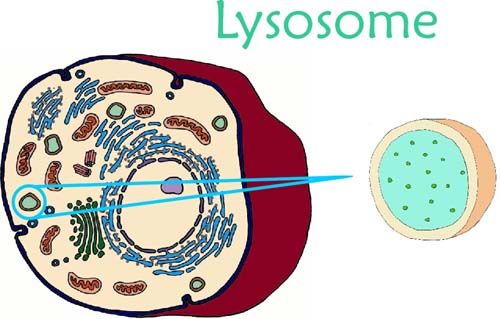
4. Lysosome
Lysosomes are organelles with separate membranes and are filled with digestive enzymes. They help digest cellular waste and maintain its wellness.
5. Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm of an animal cell is the gel-like content within the cell membrane. It contains all other organelles and encourages cellular activities to function their part.
6. Golgi Apparatus
It is a small, flat sac-like organelle within the cell. Golgi Apparatus helps sort and direct in-cell molecules to their proper destinations within or outside the cell.
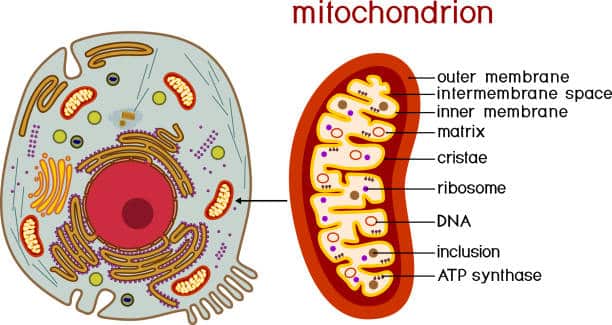
7. Mitochondrion
Mitochondria are rod-like small organelles. They are the powerhouse of an animal cell. Their function is to generate energy through cellular breathing.
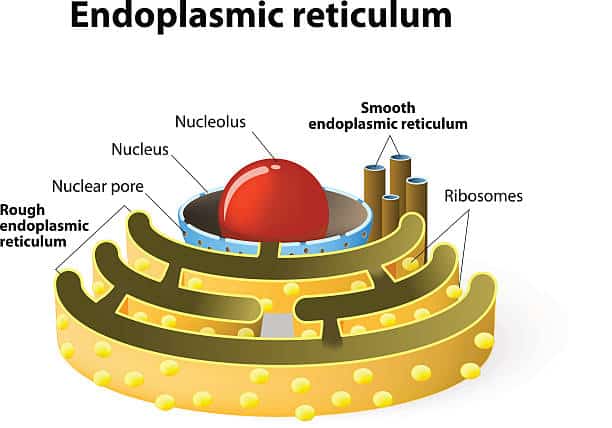
8. Ribosome
Ribosomes are cellular components that help in the process of protein synthesis. They float freely in the cytoplasm or remain attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
9. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The endoplasmic reticulum, or the ER, is a close network of membranes. They are crucial in protein synthesis, calcium storage, and more.
10. Vacuole
Food is another important function of maintaining cell health. Vacuole takes up the responsibility of strong food and water. It also helps in retaining the cell shape.
11. Nucleopore
As the name suggests, nuclepores are small open holes. Within an animal cell, they assist in successfully moving protein molecules and nucleic acid within the cell membrane.
Summing It Up
All in all, cells are the basic building blocks of an animal’s body. It takes the teamwork of several cellular organisms to maintain the finest health of any multicellular organism.
A diverse cell structure helps in the same purpose and contributes to the overall health of any species. Understanding the function of various types of cells throughout the animal body will further help aid any health issue.
Which animal cell component do you think plays the most vital role? Comment below and share with us.