Are you ready to know the list of animals whose names start with K? If yes, you’re in for a treat!
From the kangaroos to the Kob, a list of unique animals is waiting to be discovered.
Why focus on animals that start with “K,” you ask? It’s a fantastic way to increase your kids’ vocabulary and teach them animal names.
In this blog, we’ll explore the list of fascinating animals that starts with K, each accompanied by facts, small descriptions, and images.
Let’s learn more about the animals whose names start with K. We agree they are uncommon. Hence, you will be able to increase your general awareness as well.
List of Animals that Starts with K
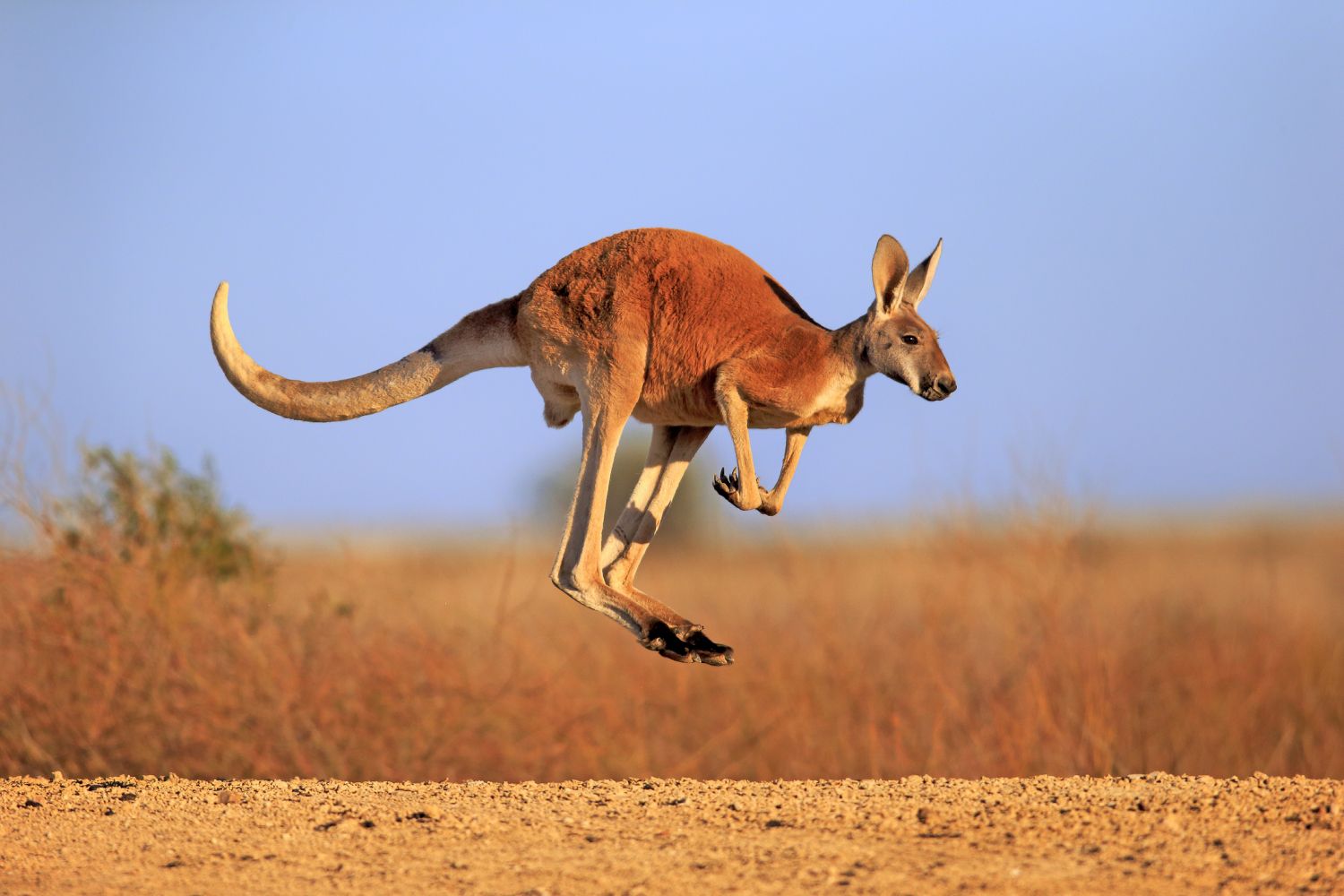
1. Kangaroo
Place of Origin: Australia
Regions of Habitat: Grasslands, forests
Scientific Name: Macropus rufus
A marsupial known for its powerful hind legs, large feet, and a tail that balances its body.
Kangaroos are adept jumpers. Kangaroos belong to the family Macropodidae, primarily found in Australia.
These unique creatures have a strong social structure, often moving in groups called “mobs,” they communicate through vocalizations and body language.
Interesting Fact: Female kangaroos have a pouch in which they carry and nurse their young.
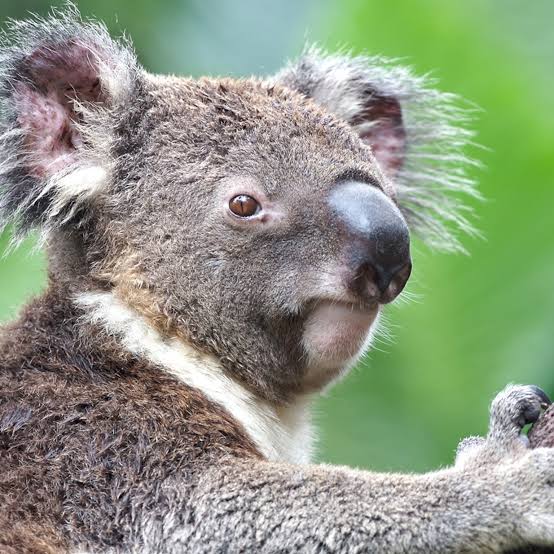
2. Koala
Place of Origin: Australia
Regions of Habitat: Eucalyptus forests
Scientific Name: Phascolarctos cinereus
The koala is an iconic Australian marsupial known for its distinct appearance and slow-paced lifestyle.
It feeds on eucalyptus leaves, which constitute almost its entire diet. Despite its teddy bear-like appearance, koalas have sharp claws and strong limbs adapted for climbing trees.
It is threatened by habitat loss and disease; conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of this beloved species.
Interesting Fact: Koalas sleep for 18-22 hours daily due to their low-energy diet.
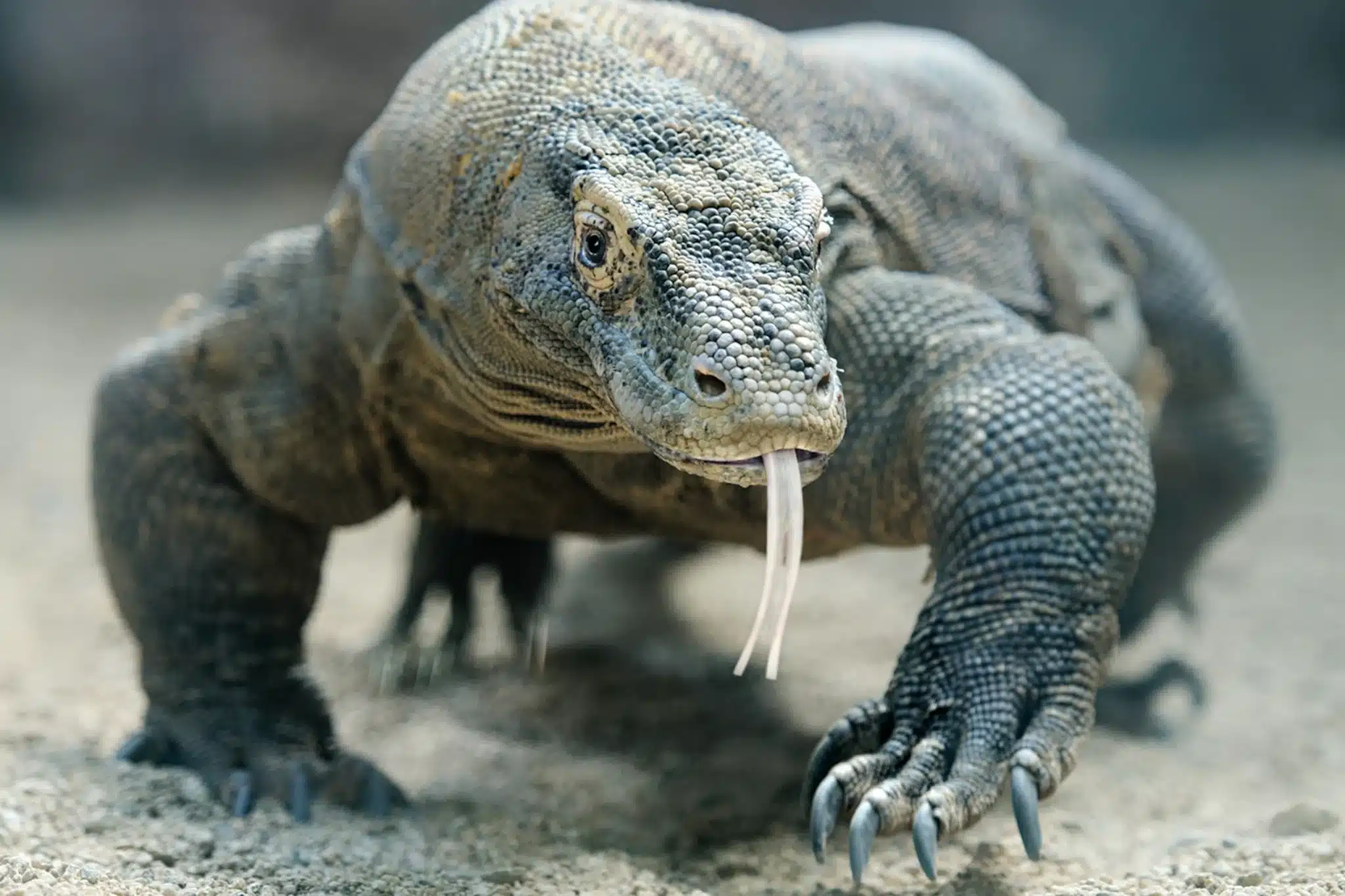
3. Komodo Dragon
Place of Origin: Indonesia
Regions of Habitat: Islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores
Scientific Name: Varanus komodoensis
The Komodo dragon is the world’s largest lizard, native to Indonesia’s Komodo Island.
It possesses powerful jaws, sharp claws, and a keen sense of smell. These carnivorous reptiles primarily hunt deer and other large prey.
Their saliva contains harmful bacteria, making their bite lethal.
Interesting Fact: Komodo dragons have a venomous bite that can be lethal to their prey.
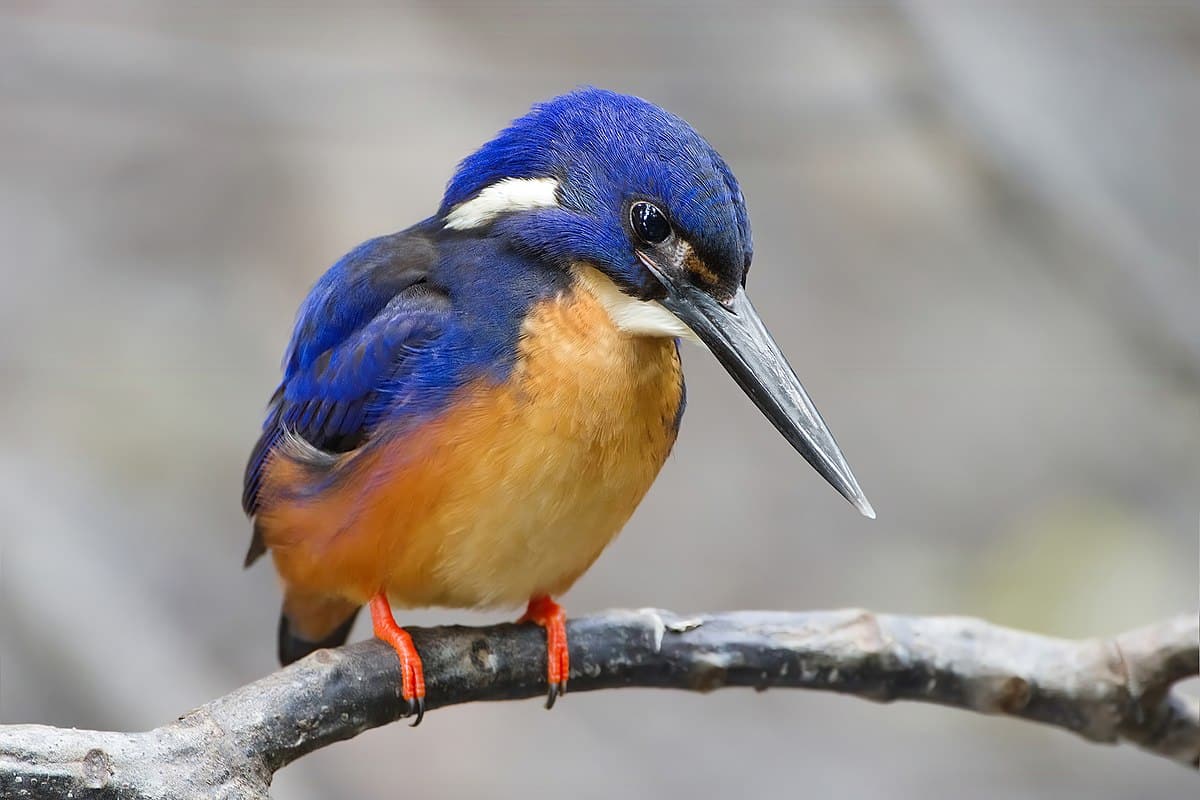
4. Kingfisher
Place of Origin: Worldwide
Regions of Habitat: Near water bodies, forests
Scientific Name: Alcedo atthis
The kingfisher is a vibrant, colorful bird known for its blue and orange color.
These agile hunters are often found near water bodies, where they dive to catch fish with remarkable precision.
They have a distinctive, long, sharp bill adapted for catching prey. The kingfisher’s call is a sharp, piercing whistle, adding to its unique charm in the natural world.
Interesting Fact: They dive into water at high speeds to catch fish, and their eyes can adjust to see underwater.
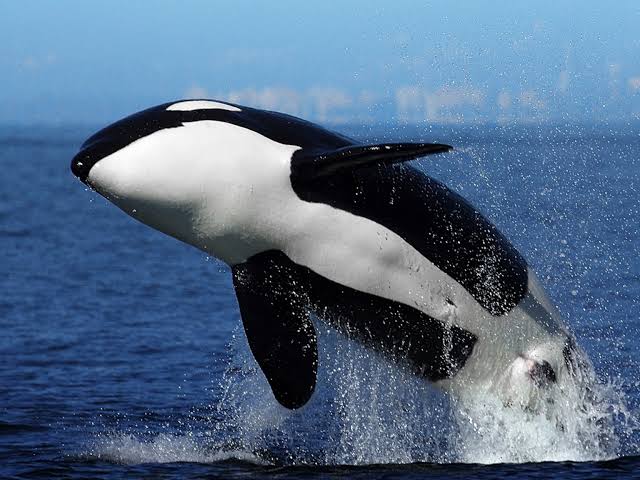
5. Killer Whale
Place of Origin: Global oceans
Regions of Habitat: Oceans, seas
Scientific Name: Orcinus orca
The killer whale is an apex predator in oceans worldwide.
Recognized by its striking black-and-white coloration, it has powerful jaws filled with sharp teeth.
Orcas are highly social animals, often traveling in pods led by a matriarch.
They have complex hunting strategies, preying on marine mammals, including seals and other whales.
Interesting Fact: Despite their name, killer whales are a type of dolphin.
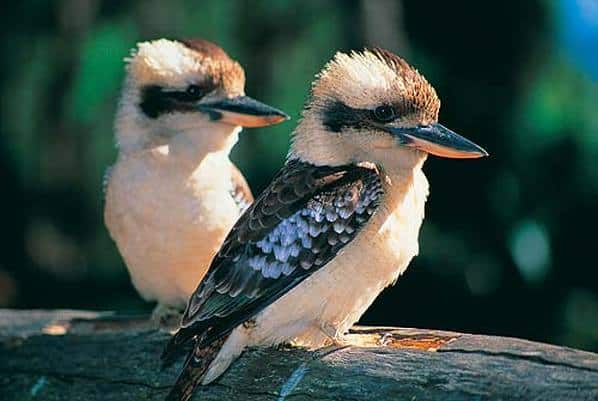
6. Kookaburra
Place of Origin: Australia, New Guinea
Regions of Habitat: Woodlands, forests
Scientific Name: Dacelo novaeguineae
The Kookaburra is a large, terrestrial kingfisher native to Australia. Known for its distinctive call, it produces a loud, echoing, laughter-like sound often heard at dawn and dusk.
It has a robust body with a large head, strong beak, and short wings.
It feeds primarily on insects, reptiles, and small mammals and is vital in controlling pest populations.
Interesting Fact: Kookaburras’ laughing call is often mistaken for human laughter.
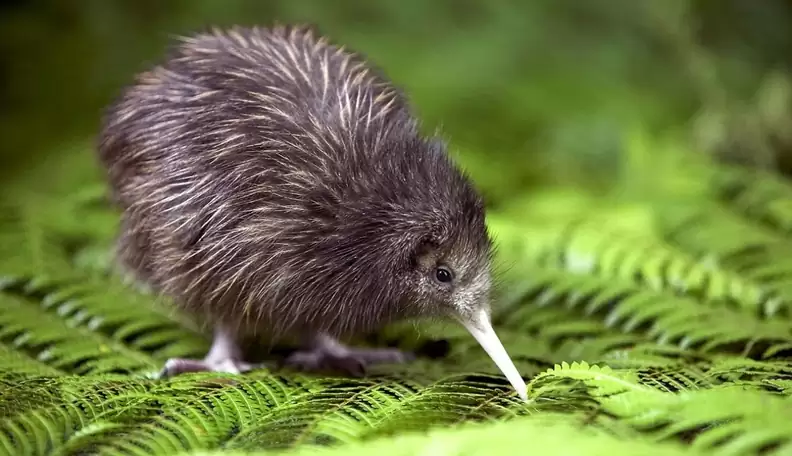
7. Kiwi
Place of Origin: New Zealand
Regions of Habitat: Forests, grasslands
Scientific Name: Apteryx
The kiwi is a flightless bird native to New Zealand, known for its unique appearance and nocturnal habits.
It has a long, slender bill, dense brown plumage, and tiny wings hidden beneath its feathers.
Kiwis are primarily carnivorous, feeding on insects, worms, and occasionally fruits.
Due to habitat loss and introduced predators, many species of kiwi are endangered, and conservation efforts are underway to protect them.
Interesting Fact: Kiwi birds lay the largest eggs relative to the body size of any bird species.
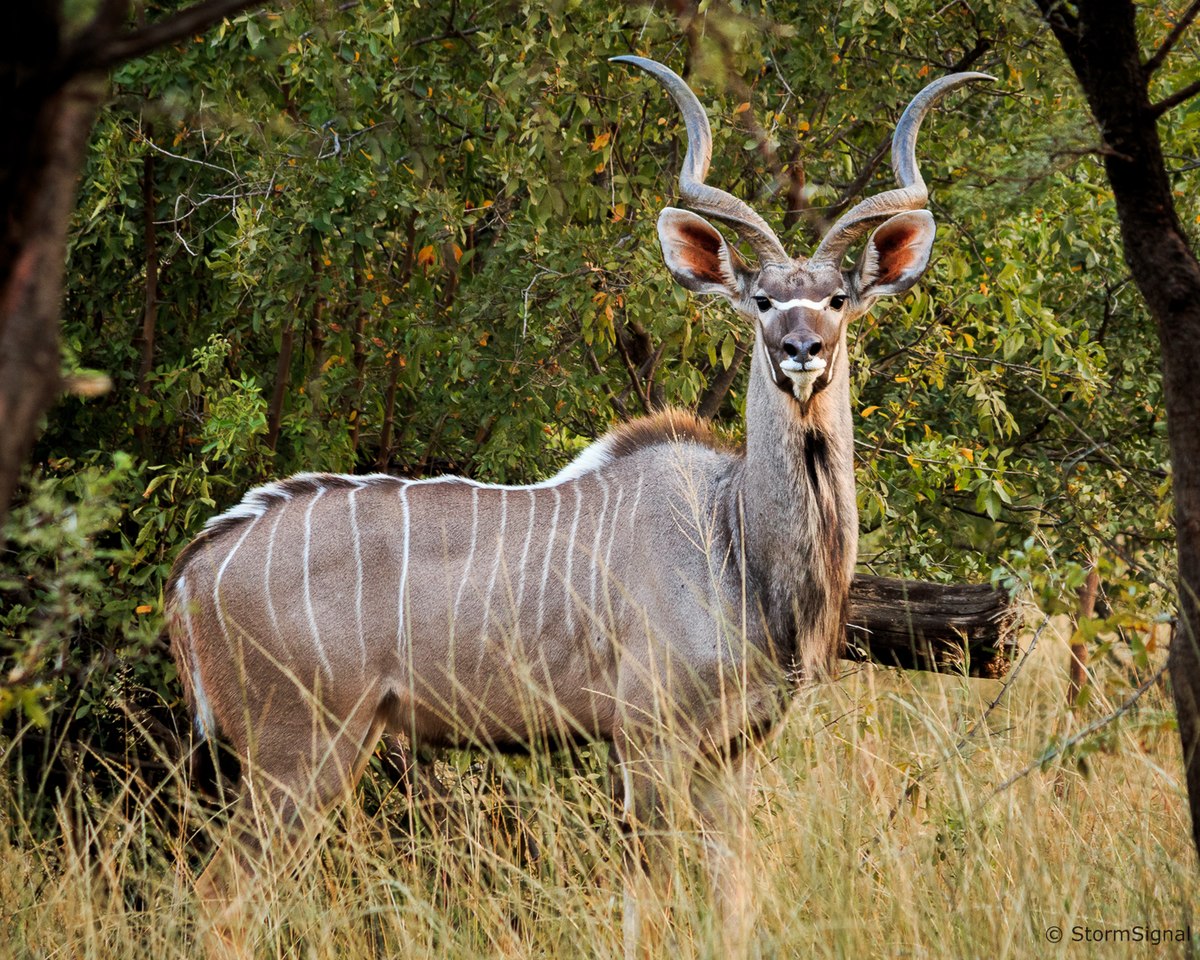
8. Kudu
Place of Origin: Africa
Regions of Habitat: Savannahs, woodlands
Scientific Name: Tragelaphus strepsiceros
The kudu is a type of antelope found in eastern and southern Africa.
They are known for their long, spiral horns; the male kudu possesses impressive, twisted antlers.
These antlers can reach up to 72 inches in length, making them one of the most distinctive features of the animal.
Kudus are primarily browsers, feeding on leaves, shoots, and fruits in their natural habitat.
Interesting Fact: Male kudus have a beard under their chin and a series of white stripes on their body.
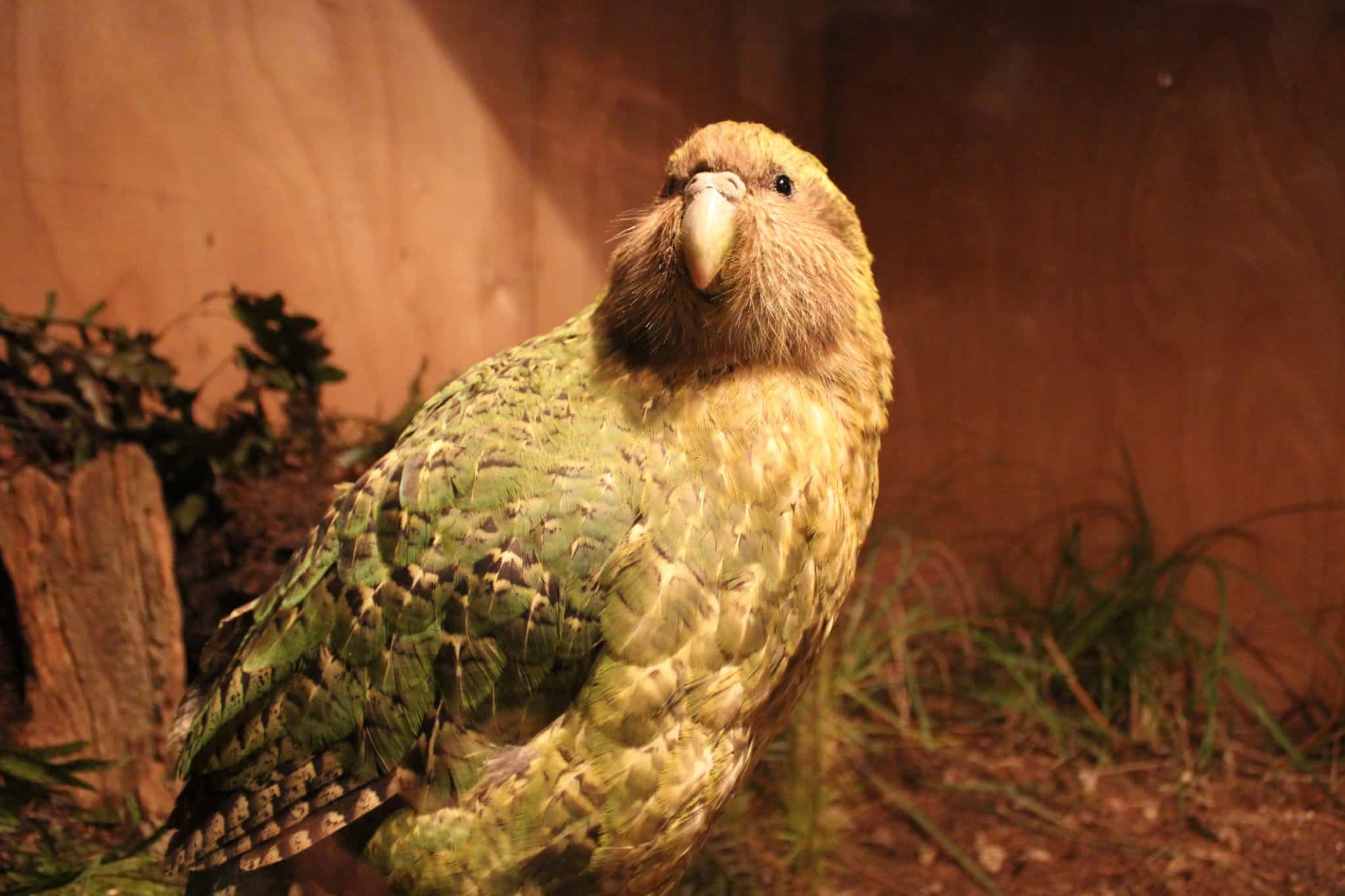
9. Kakapo
Place of Origin: New Zealand
Regions of Habitat: Forests
Scientific Name: Strigops habroptilus
The kakapo, the “owl parrot,” is a critically endangered flightless bird native to New Zealand.
It is famous for its nocturnal habits and distinctive moss-green plumage.
Once abundant, the kakapo population has dwindled due to habitat loss and introduced predators.
Conservation efforts aim to protect and increase the species’ numbers.
Interesting Fact: Kakapos are known for their peculiar mating calls and inability to fly.
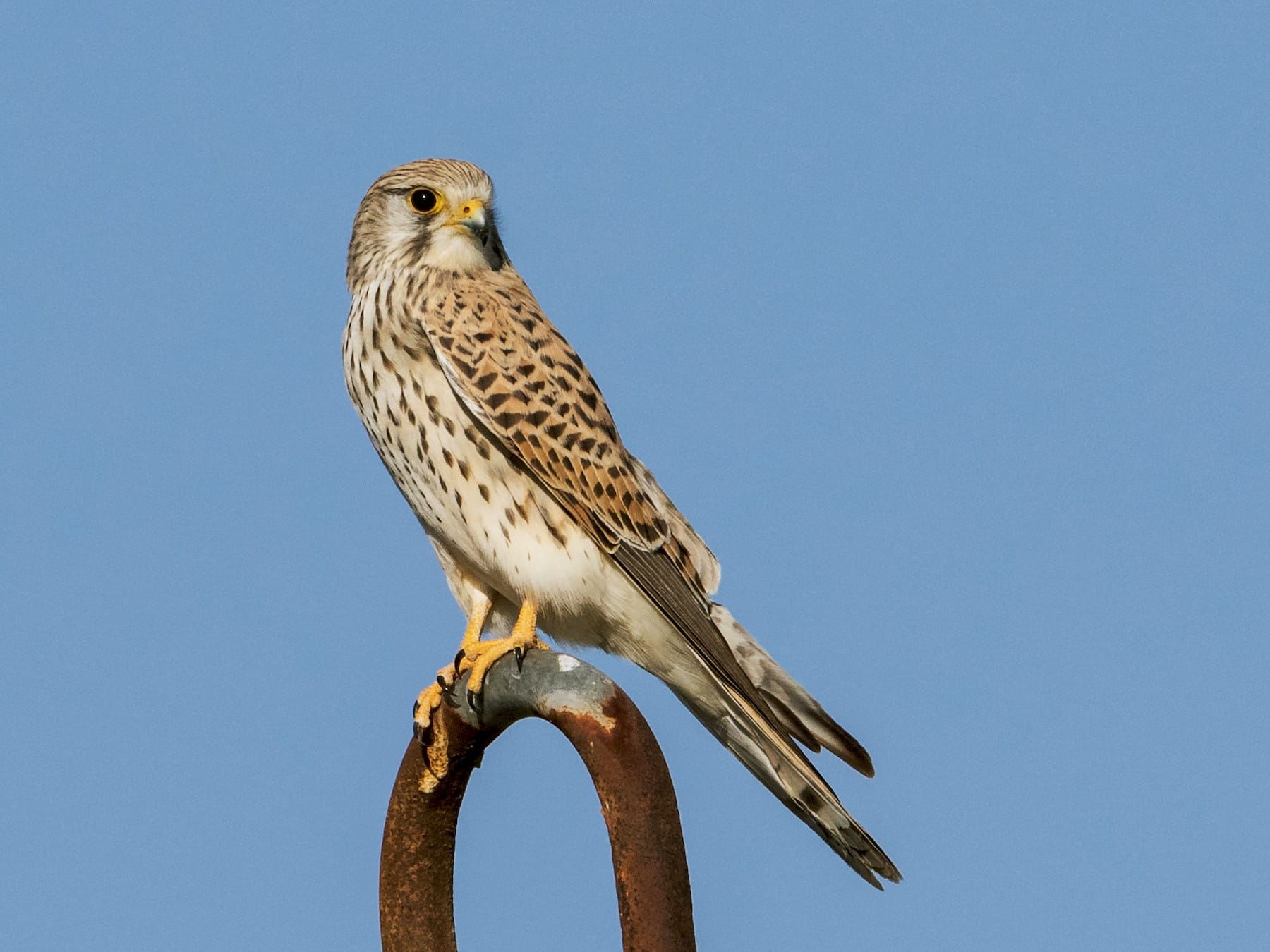
10. Kestrel
Place of Origin: Worldwide
Regions of Habitat: Open lands, grasslands
Scientific Name: Falco tinnunculus
The Kestrel is a small and agile bird of prey.
It is known for its hovering flight while hunting for prey. Its distinctive pointed wings and long tail make it adept at catching insects, small mammals, and birds.
The kestrel’s keen eyesight and swift movements make it a dangerous hunter in diverse habitats worldwide.
Interesting Fact: Kestrels can see ultraviolet light, which helps them detect the trails of voles.
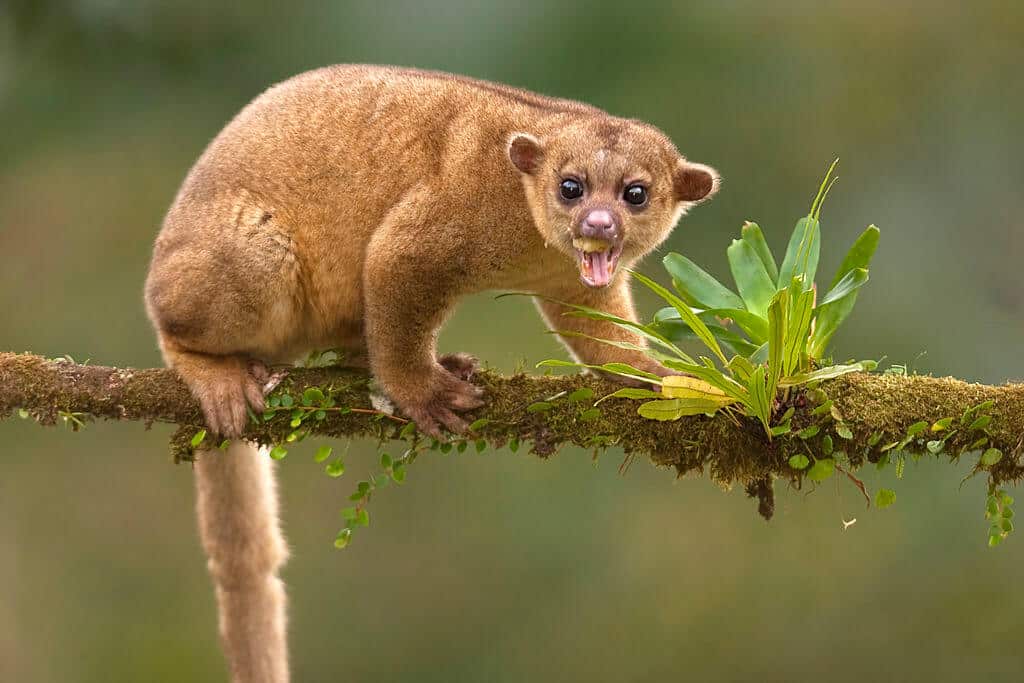
11. Kinkajou
Place of Origin: Central and South America
Regions of Habitat: Tropical rainforests
Scientific Name: Potos flavus
The kinkajou is a small mammal native to Central and South America.
It has a golden or brownish fur, a long prehensile tail, and large, round eyes.
They are primarily nocturnal; they spend their nights foraging for fruit and occasionally hunting insects.
Despite its cute appearance, it possesses sharp claws and can be aggressive when threatened.
Interesting Fact: Kinkajous have a long tongue that helps them extract nectar from flowers, much like some species of birds.
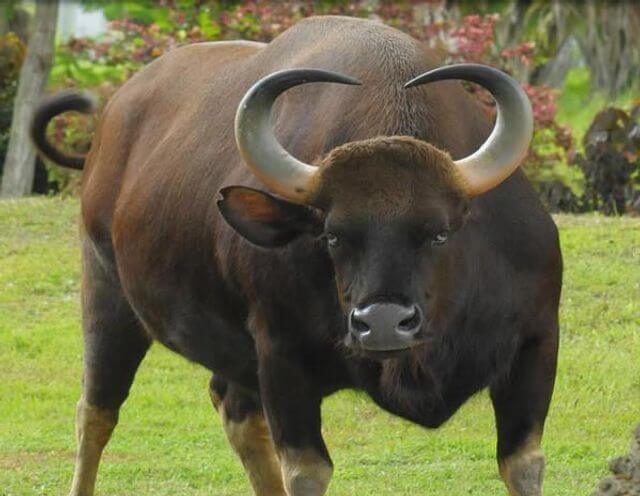
12. Kouprey
Place of Origin: Southeast Asia
Regions of Habitat: Grasslands, forests
Scientific Name: Bos sauveli
The Kouprey is a rare wild ox native to Southeast Asia.
It possesses a distinctive tall and narrow body with a dark chestnut coat.
This species is critically endangered, with its population dwindling due to habitat loss and hunting.
Efforts are ongoing to conserve and protect this unique and iconic creature.
Interesting Fact: The Kouprey is often called the “Cambodian forest ox.”
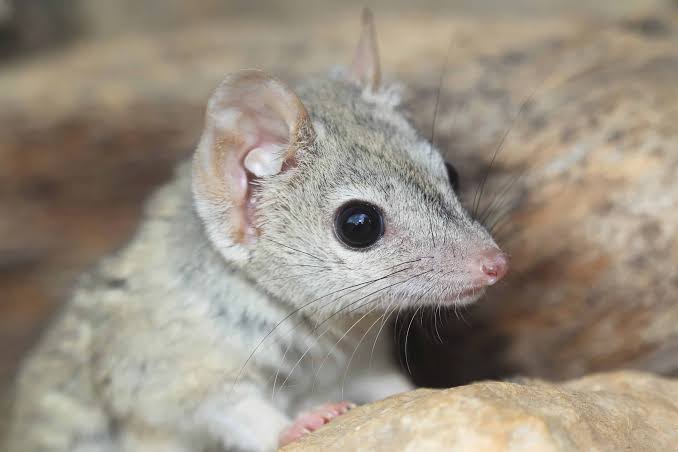
13. Kowari
Place of Origin: Australia
Regions of Habitat: Deserts, arid regions
Scientific Name: Dasyuroides byrnei
Kowari is a species of dasyurid, a group of carnivorous marsupials native to Australia.
This small, nocturnal creature has a distinctive coat pattern of white spots on a brown or gray background.
It primarily feeds on insects, small vertebrates, and fruits.
Due to habitat loss and predation, the Kowari is considered vulnerable in the wild.
Interesting Fact: Kowaris have large eyes adapted for nocturnal hunting.
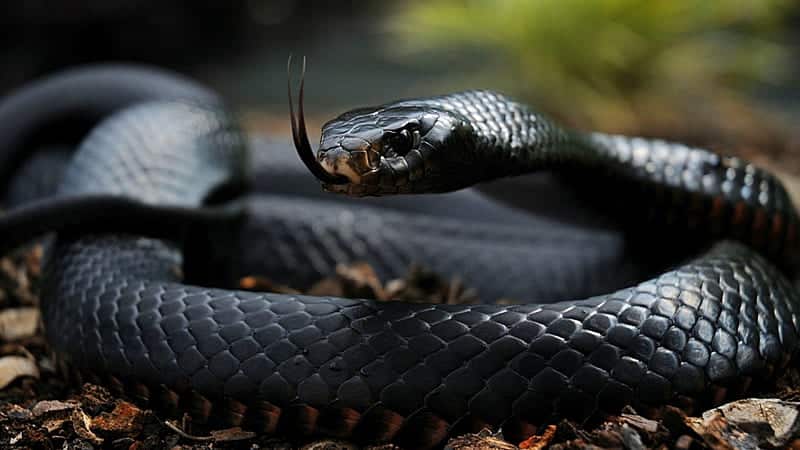
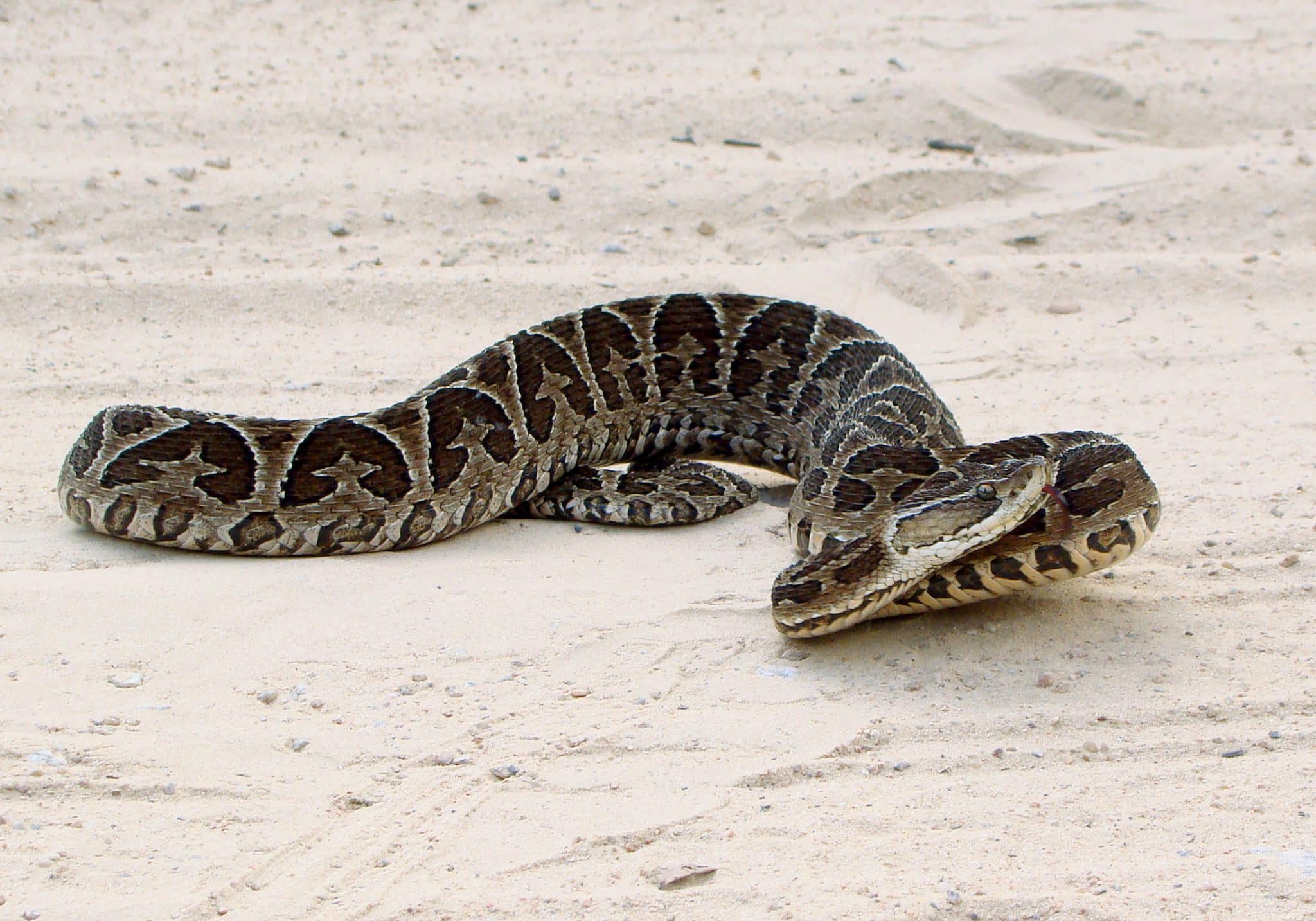
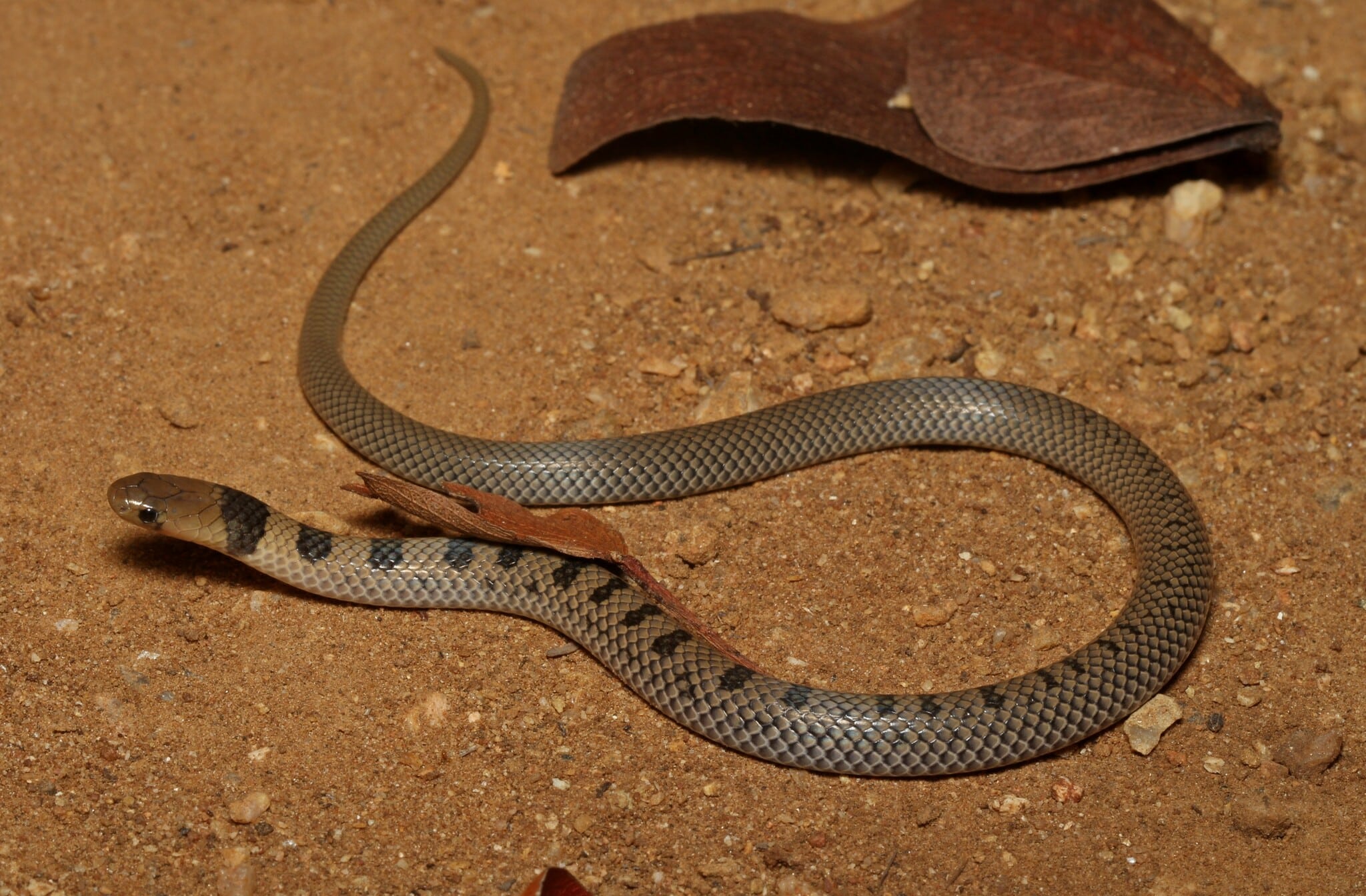
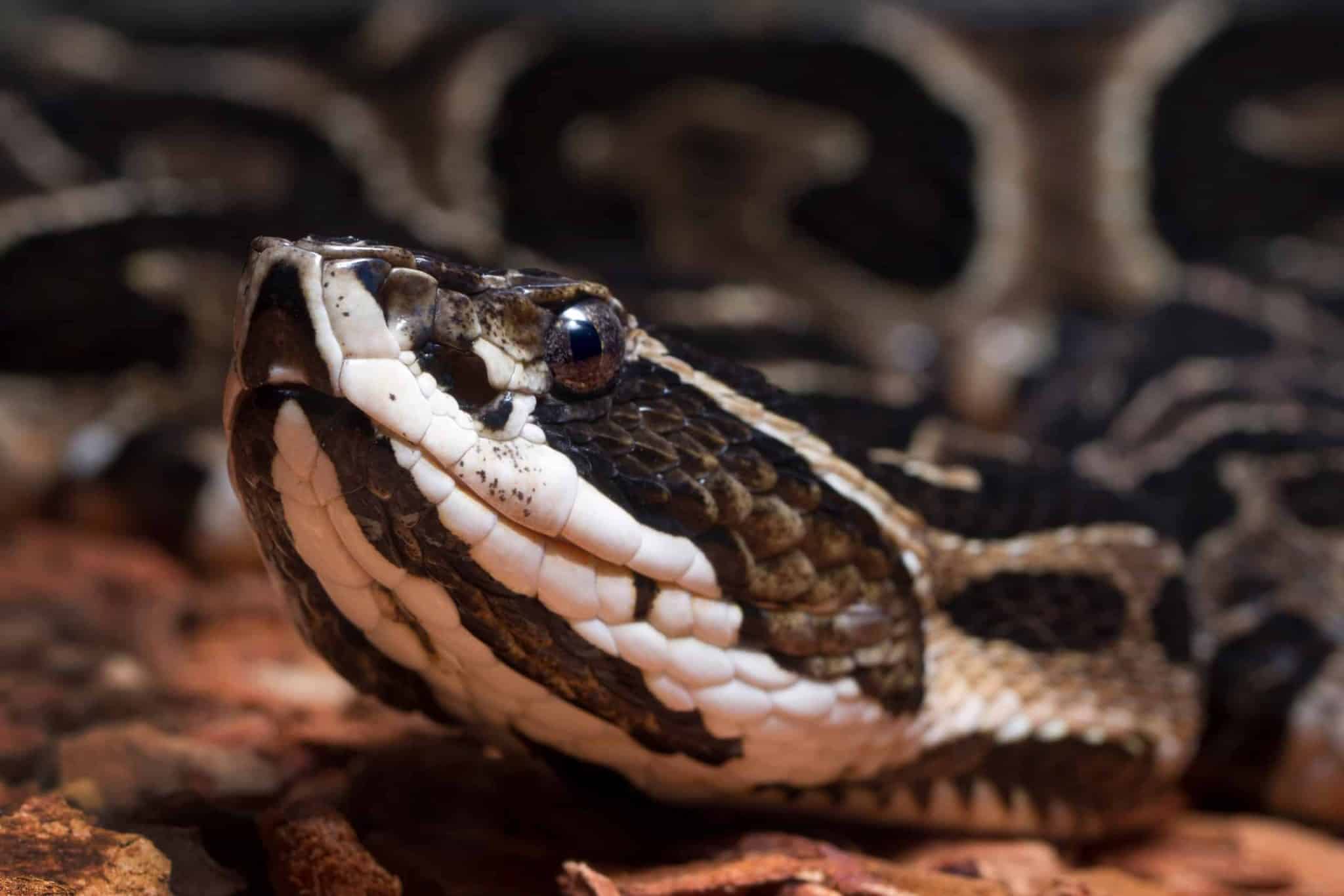
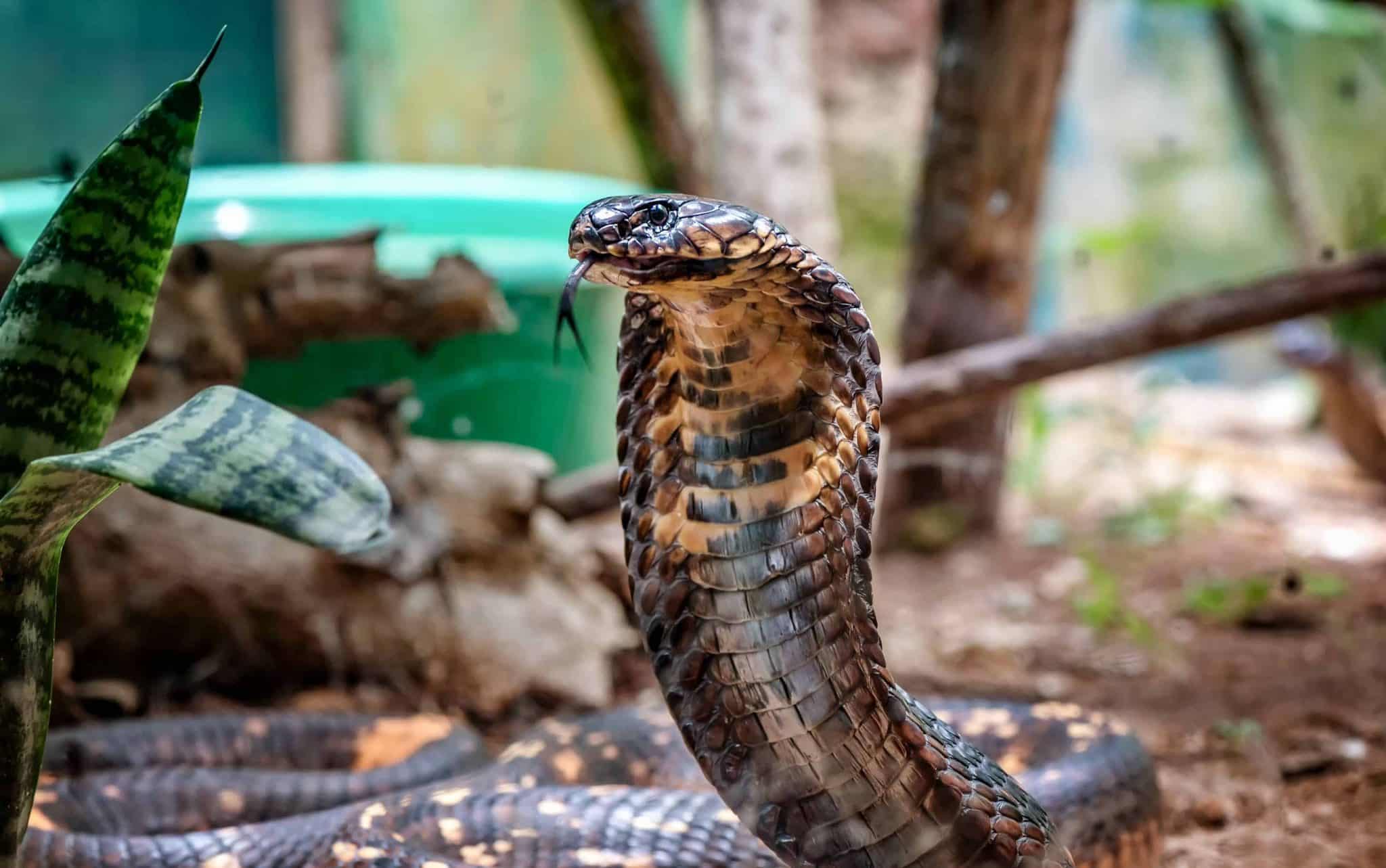
14. King Cobra
Place of Origin: Southeast Asia
Regions of Habitat: Forests, grasslands
Scientific Name: Ophiophagus Hannah
The King Cobra, scientifically known as “Ophiophagus hannah,” is the world’s longest venomous snake, reaching lengths of up to 18 feet (5.5 meters).
They are renowned for their potent neurotoxic venom; a single bite can deliver enough toxin to kill an elephant or 20 people.
Despite its fearsome reputation, the King Cobra primarily preys on other snakes, showcasing its specialized diet and predatory prowess.
Interesting Fact: King cobras are the only snakes that build nests for their eggs.
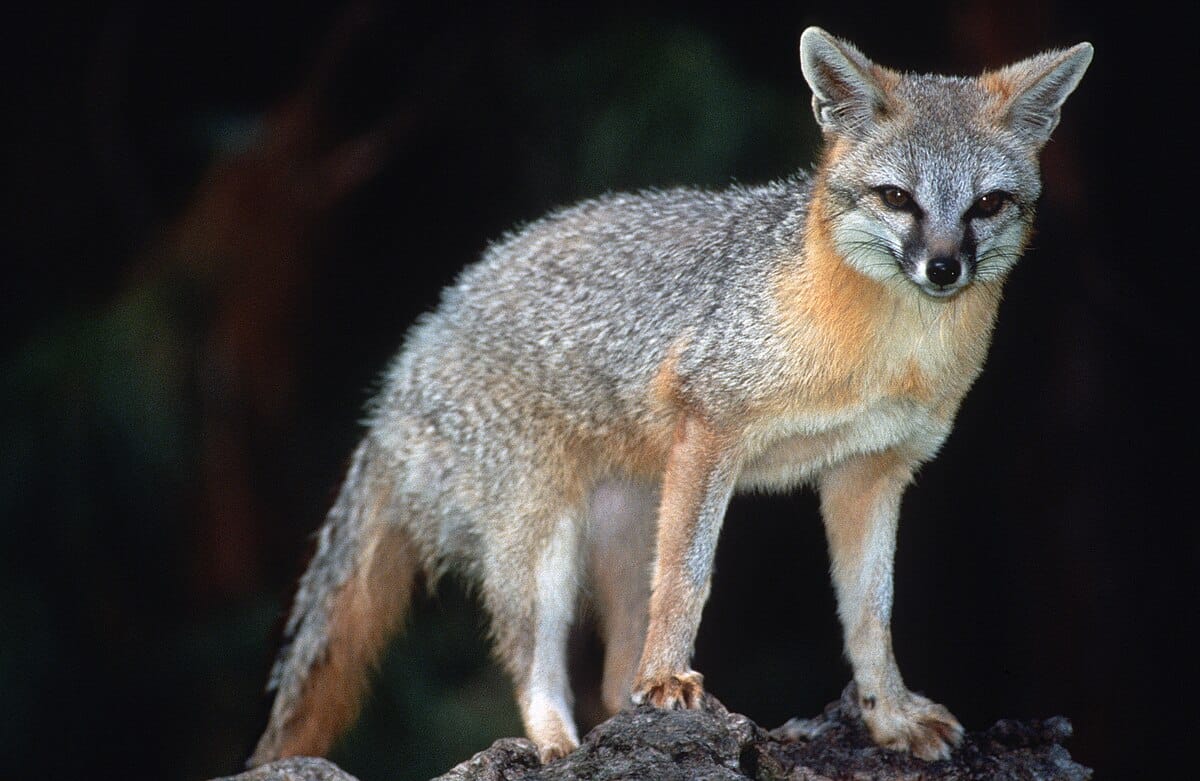
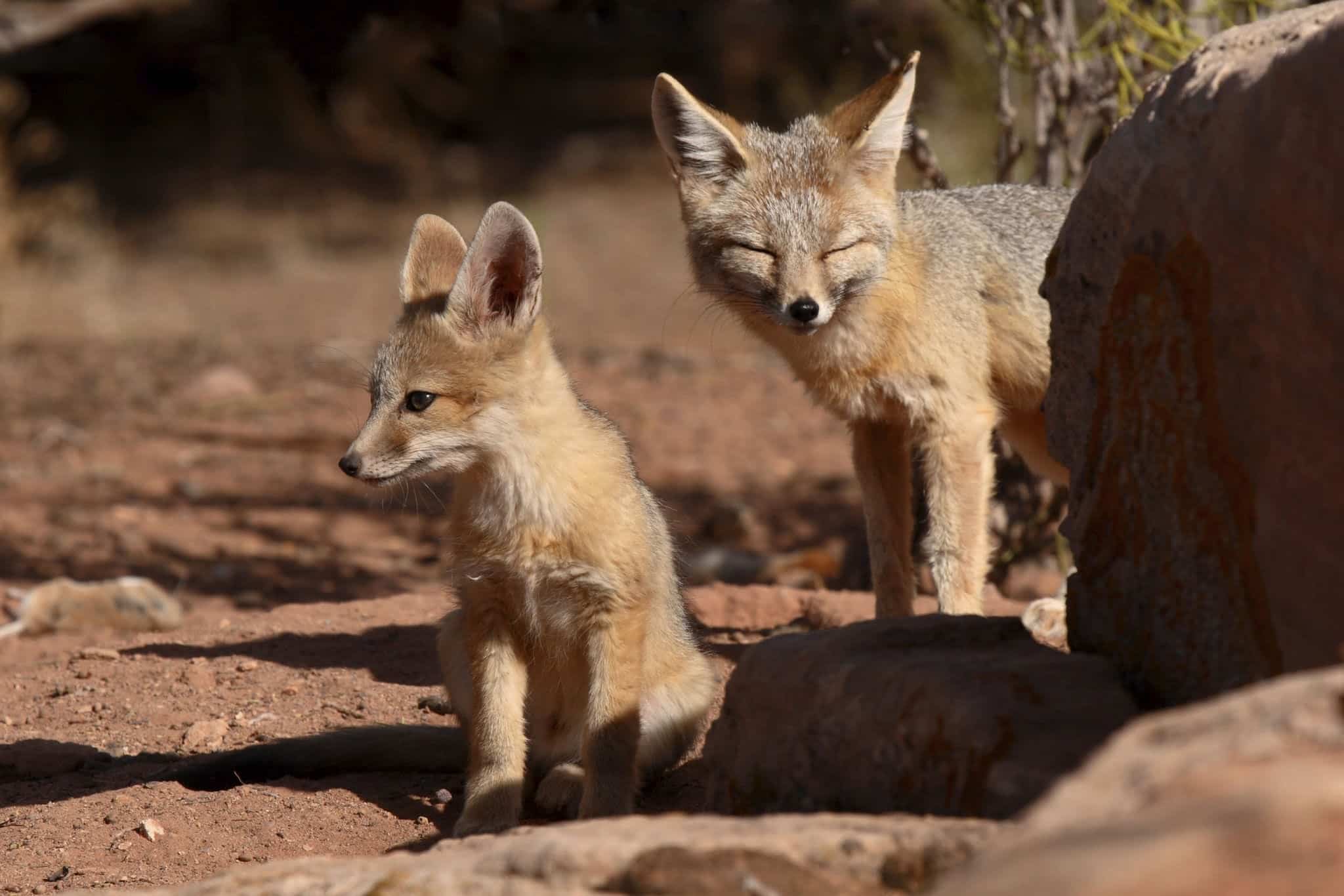
15. Kit Fox
Place of Origin: North America
Regions of Habitat: Deserts, scrublands
Scientific Name: Vulpes macrotis
The kit fox (Vulpes macrotis) is a small species of fox found in North America’s desert regions.
It has large ears that help dissipate heat and detect prey underground.
Nocturnal kit foxes are typically skilled hunters, primarily consuming small mammals, birds, and insects.
Conservation efforts are in place due to habitat loss and fragmentation threatening their populations.
Interesting Fact: Kit foxes can survive without drinking water, obtaining all the moisture they need from their prey.
16. Kakawahie
Place of Origin: Hawaii
Regions of Habitat: Forests, mountains
Scientific Name: Paroreomyza flammea
Kakawahie, also known as the Hawaiian Stilt, is a slender, long-legged bird native to Hawaii’s wetlands and coastal areas.
It boasts a distinctive black-and-white plumage, with long, pink legs adding to its elegant appearance.
This species is primarily carnivorous, feeding small aquatic creatures like insects and crustaceans.
Conservation efforts are crucial for the Kakawahie due to habitat loss and other threats.
Interesting Fact: The kakawahie is one of the rarest birds in Hawaii, with only a few hundred individuals remaining.
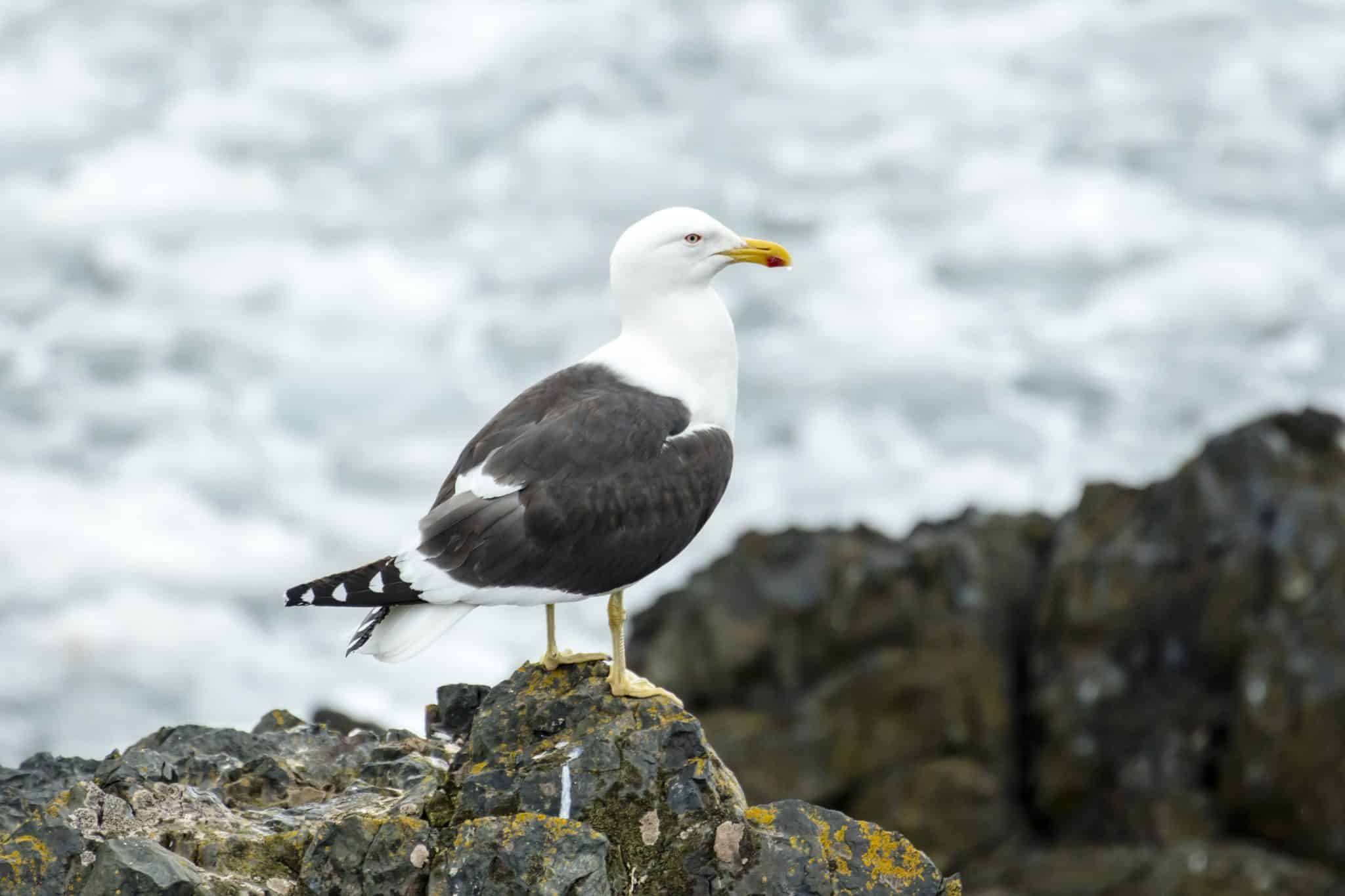
17. Kelp Gull
Place of Origin: Coastal regions worldwide
Regions of Habitat: Coastlines, islands
Scientific Name: Larus dominicanus
The Kelp Gull is a large seabird found mainly in the Southern Hemisphere.
It has a black and white plumage with a yellow bill and legs. These gulls are opportunistic feeders, often scavenging for food along coastlines.
They are known for their loud calls and adaptability to various marine environments.
Interesting Fact: Kelp gulls are opportunistic feeders and often scavenge food from human settlements.
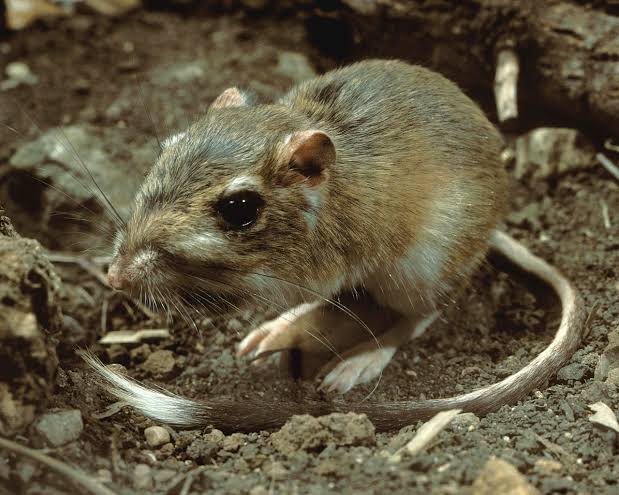
18. Kangaroo Rat
Place of Origin: North America
Regions of Habitat: Deserts, grasslands
Scientific Name: Dipodomys spp.
The kangaroo rat is a small rodent native to North America’s deserts.
It is known for its remarkable agility and can leap up to nine feet in a single bound.
Its large hind legs and long tail aid in balance and jumping.
Adapted to arid conditions, it obtains most of its water from the seeds it consumes.
Interesting Fact: Kangaroo rats can survive without drinking water, obtaining moisture from the seeds they consume.
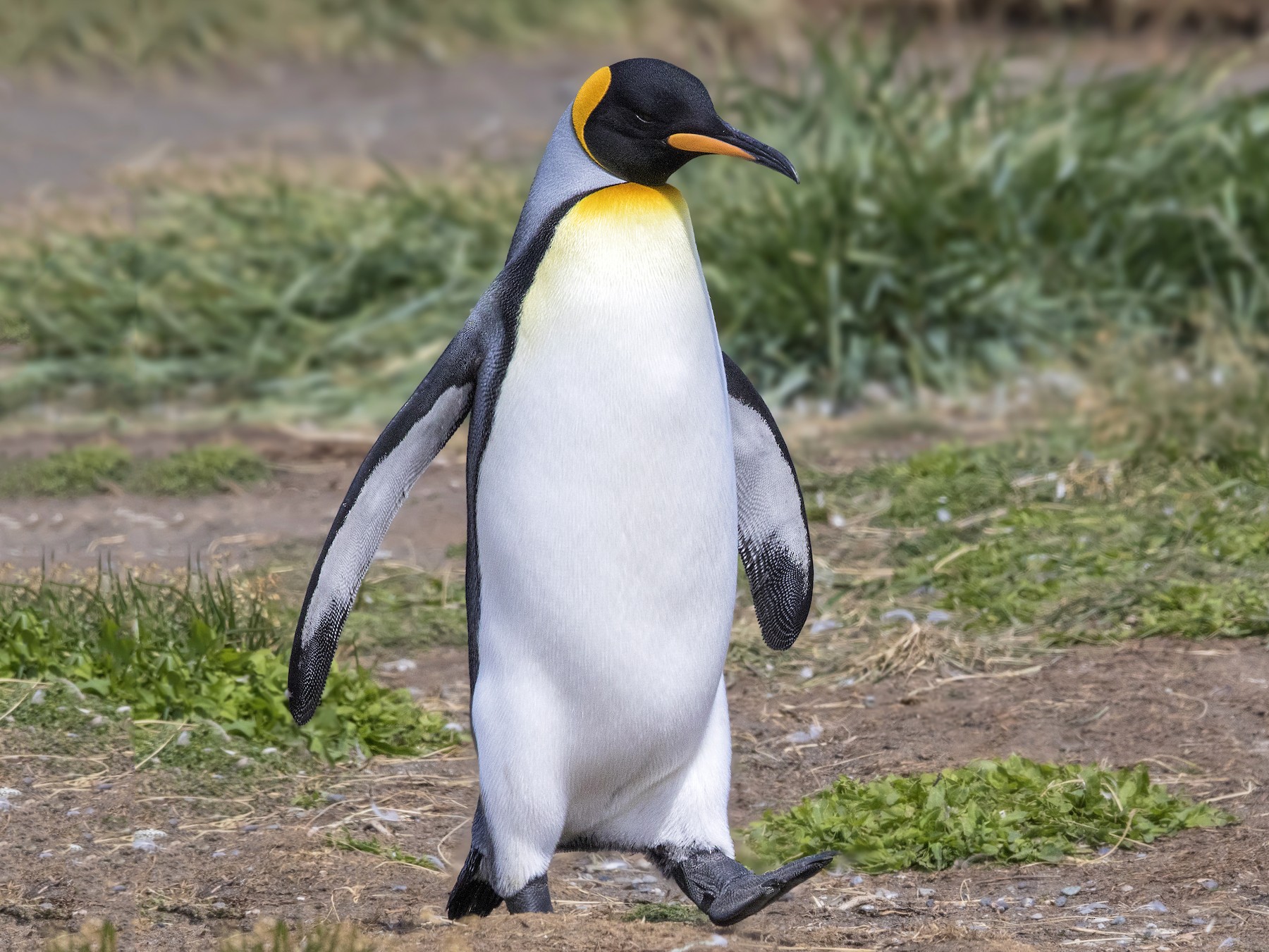
19. King Penguin
Place of Origin: Sub-Antarctic regions
Regions of Habitat: Islands, coastlines
Scientific Name: Aptenodytes patagonicus
The King Penguin is the second-largest species, surpassed only by the Emperor Penguin.
It has a distinct appearance with a bright orange patch on its neck and upper chest. Native to the subantarctic regions, these penguins are excellent swimmers who can dive to great depths for food.
They form large colonies for breeding purposes and show dedicated parental care for their chicks.
Interesting Fact: King penguins can dive to depths of over 300 meters in search of food.
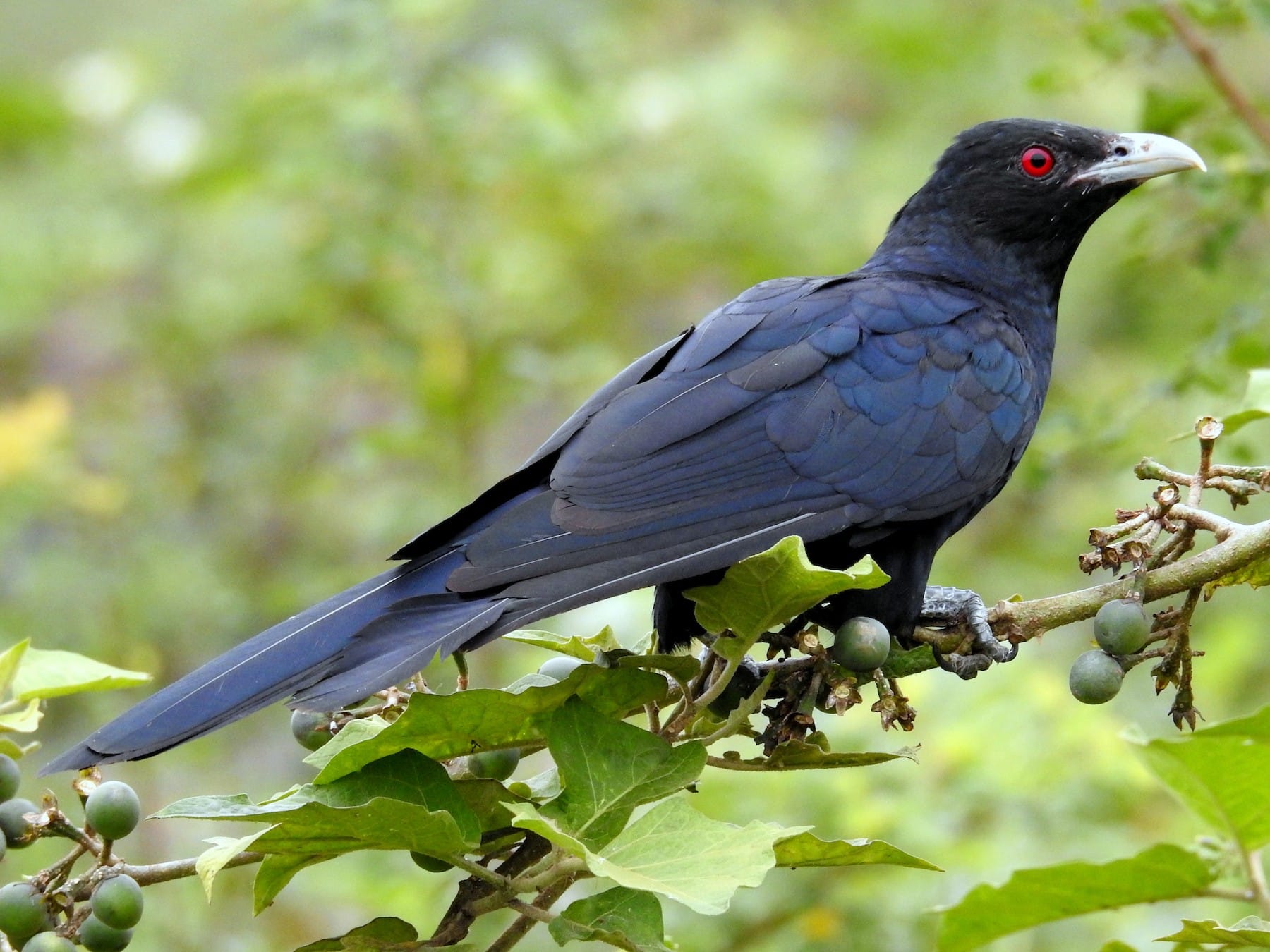
20. Koel
Place of Origin: Asia, Australia
Regions of Habitat: Forests, urban areas
Scientific Name: Eudynamys spp.
The koel bird, also known as the Asian koel, is a member of the cuckoo family.
Males are glossy black with striking red eyes, while females are brown with a heavily streaked appearance.
They are renowned for their loud and distinctive call, often heard during the breeding season.
Koels primarily feed on fruits, making them essential seed dispersers in their habitats.
Interesting Fact: Koels are brood parasites, laying their eggs in the nests of other bird species.
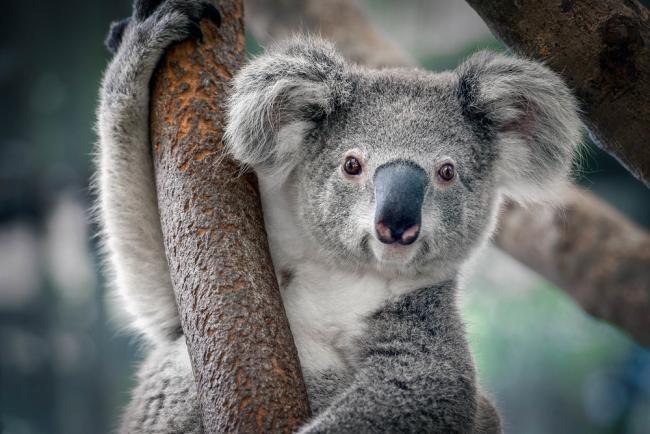
21. Koala
Place of Origin: Australia
Regions of Habitat: Eucalyptus forests
Scientific Name: Phascolarctos cinereus
The koala is an iconic marsupial native to Australia. Recognized by its fluffy grey fur, large ears, and distinctive black nose, it spends most of its time in eucalyptus trees.
Koalas primarily eat eucalyptus leaves, providing them with nutrition and hydration.
Due to habitat loss and other threats, they are considered a vulnerable species in the wild.
Interesting Fact: Koalas sleep for 18-22 hours daily due to their low-energy diet.
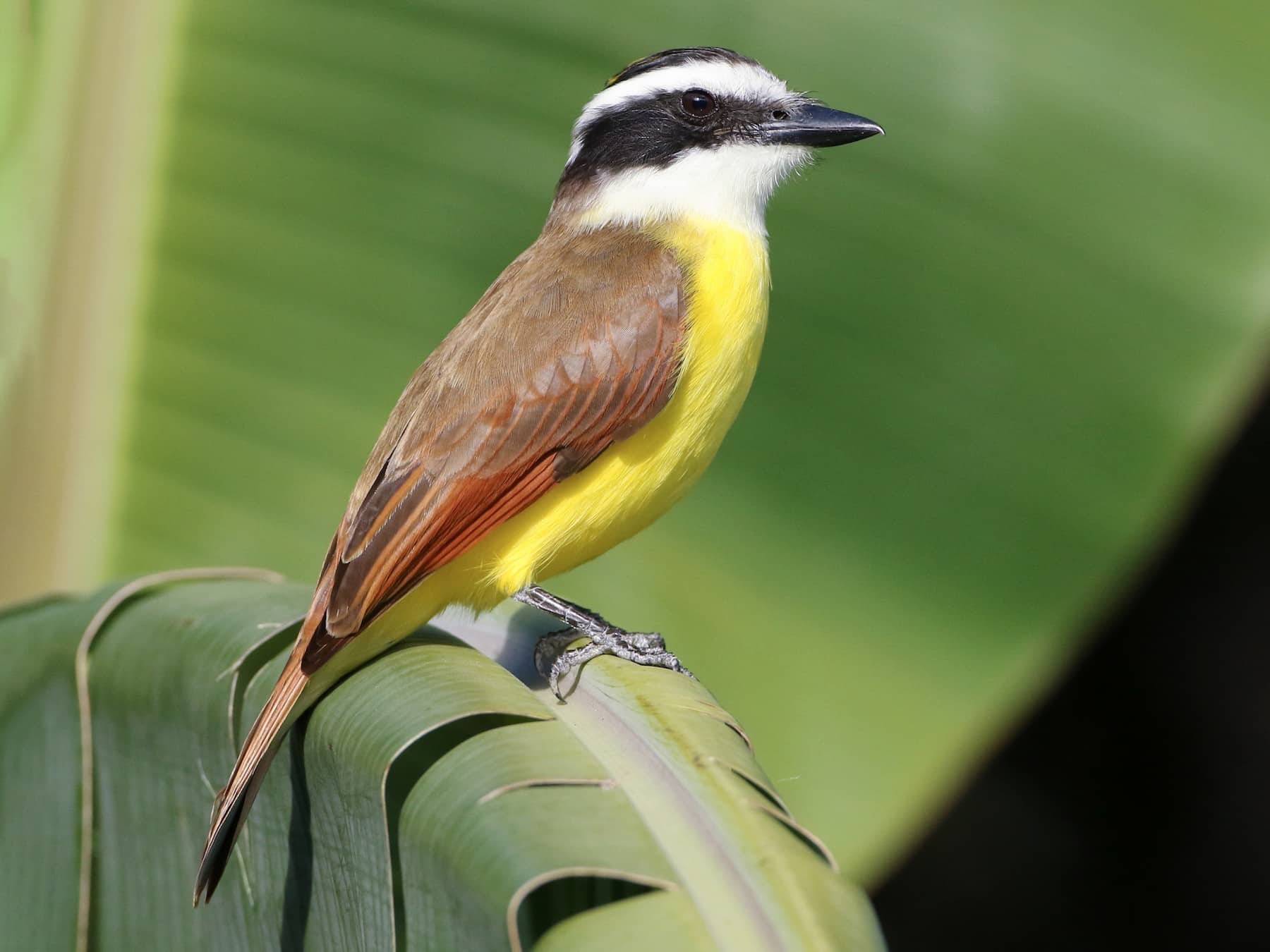
22. Kiskadee
Place of Origin: Americas
Regions of Habitat: Woodlands, wetlands
Scientific Name: Pitangus spp.
Kiskadees are vibrant, medium-sized birds known for their striking yellow and black plumage.
They have a distinct call often described as “kis-ka-dee,” from which they derive their name.
Native to the Americas, these birds are commonly found in open woodlands, gardens, and urban areas.
Their diet primarily consists of insects, fruits, and small vertebrates.
Interesting Fact: Kiskadees are known for their loud and varied vocalizations, often heard throughout the day.
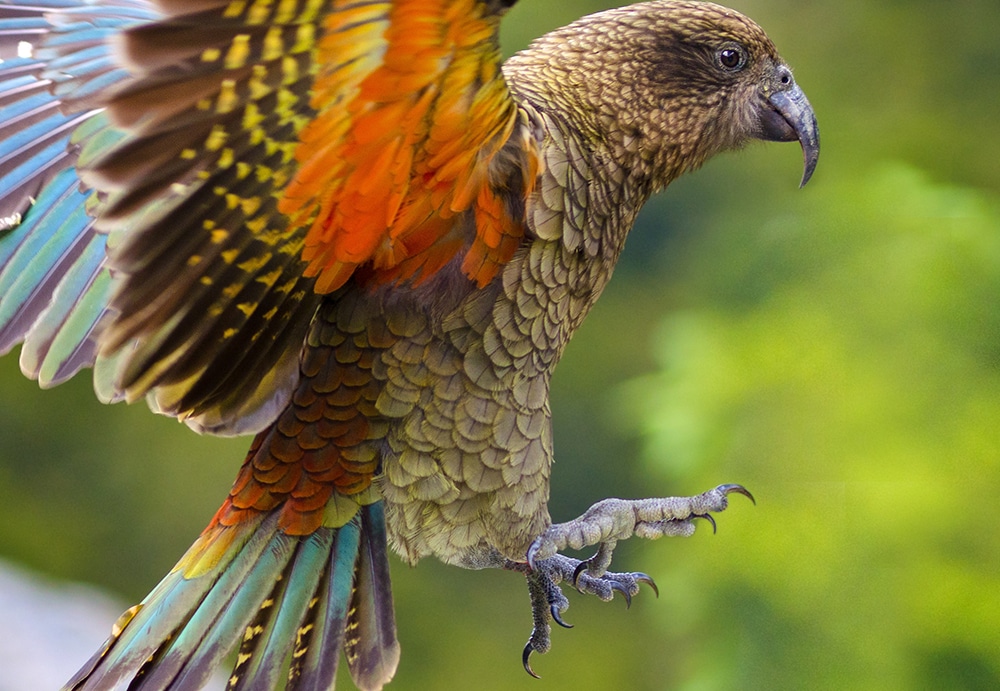
23. Kea
Place of Origin: New Zealand
Regions of Habitat: Mountains, forests
Scientific Name: Nestor notabilis
Kea is a species of large, intelligent parrots native to New Zealand’s forested regions.
They are known for their curiosity and playful nature and are adept at problem-solving and using tools.
Keas have vibrant olive-green plumage with bright orange underwings, making them visually striking.
Unfortunately, they are classified as endangered due to habitat loss and predation.
Interesting Fact: Keas are notorious for their mischievous nature, often exploring and sometimes damaging human belongings.
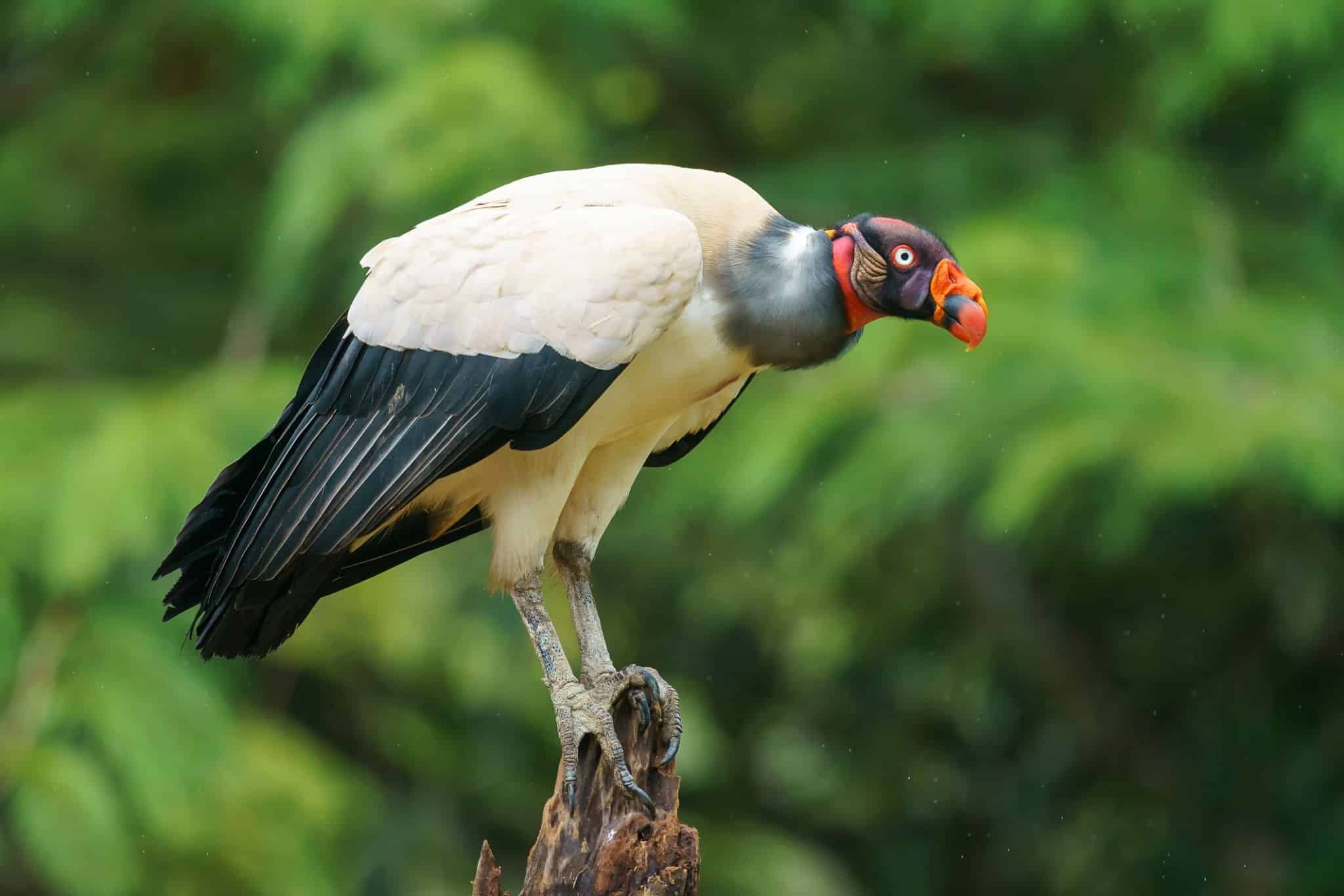
24. King Vulture
Place of Origin: Central and South America
Regions of Habitat: Tropical forests, savannas
Scientific Name: Sarcoramphus papa
The King Vulture is a striking bird known for its colorful appearance and large size.
Its feathers display a mix of white and black and touches of red, orange, and yellow.
This vulture possesses a powerful beak designed for tearing flesh and plays a crucial role in cleaning up carcasses in its habitat.
They are found in Central and South America. They often soar high in the sky, utilizing thermal currents to glide effortlessly.
Interesting Fact: King vultures have a keen sense of smell, allowing them to detect carrion from great distances.
25. Kelpie
Place of Origin: Scotland
Regions of Habitat: Mythical creature
Scientific Name: Mythological
The Kelpie is a mythical water spirit or shape-shifting creature from Scottish folklore.
Often appearing as a horse, it lures unsuspecting travelers, especially children, into water bodies to drown them.
Some tales depict it as a powerful and cunning entity, capable of manipulating its appearance to deceive.
Legend warns of its treacherous nature as a cautionary tale for those venturing near water alone.
Interesting Fact: The legend of the Kelpie is deeply rooted in Scottish mythology, with various tales describing its appearance and behavior.
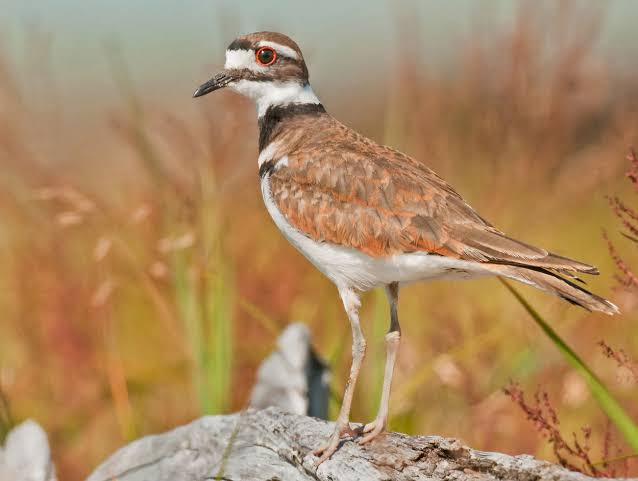
26. Killdeer
Place of Origin: North and South America
Regions of Habitat: Grasslands, shorelines
Scientific Name: Charadrius vociferus
The Killdeer is a medium-sized plover known for its distinctive double breast band.
It has a brownish upper body and a white underbelly. One of its unique behaviors is the “broken-wing display” used to distract predators away from its nest.
Found in open areas like fields and shorelines, the Killdeer is widespread across North and South America.
Interesting Fact: Killdeers often feign injury to distract predators away from their nests.
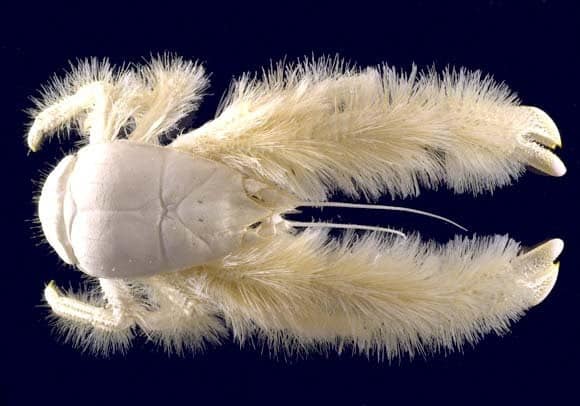
27. Kiwa
Place of Origin: Deep-sea hydrothermal vents
Regions of Habitat: Ocean floor
Scientific Name: Kiwa spp.
Kiwa is a genus of marine decapod crustaceans known for their distinctive appearance.
These animals are often found in deep-sea hydrothermal vents. They possess striking features, including hairy appendages and large, pincer-like claws.
Kiwa species are adapted to extreme environments, showcasing the wonders of deep-sea biodiversity.
Interesting Fact: Kiwa crabs thrive in extreme environments, with some species living near hydrothermal vents.
28. Kultarr
Place of Origin: Australia
Regions of Habitat: Deserts
Scientific Name: Antechinomys laniger
The kultarr (Antechinomys laniger) is a small, nocturnal marsupial native to Australia.
It has a distinctive, sandy-colored fur and a slender, elongated body, allowing it to move swiftly through its arid habitat.
Primarily insectivorous, it preys on various insects and other small invertebrates.
Due to its secretive nature and nocturnal habits, the kultarr is seldom seen by humans.
Interesting Fact: Kultarrs are agile climbers, using their sharp claws to scale trees and rocks.
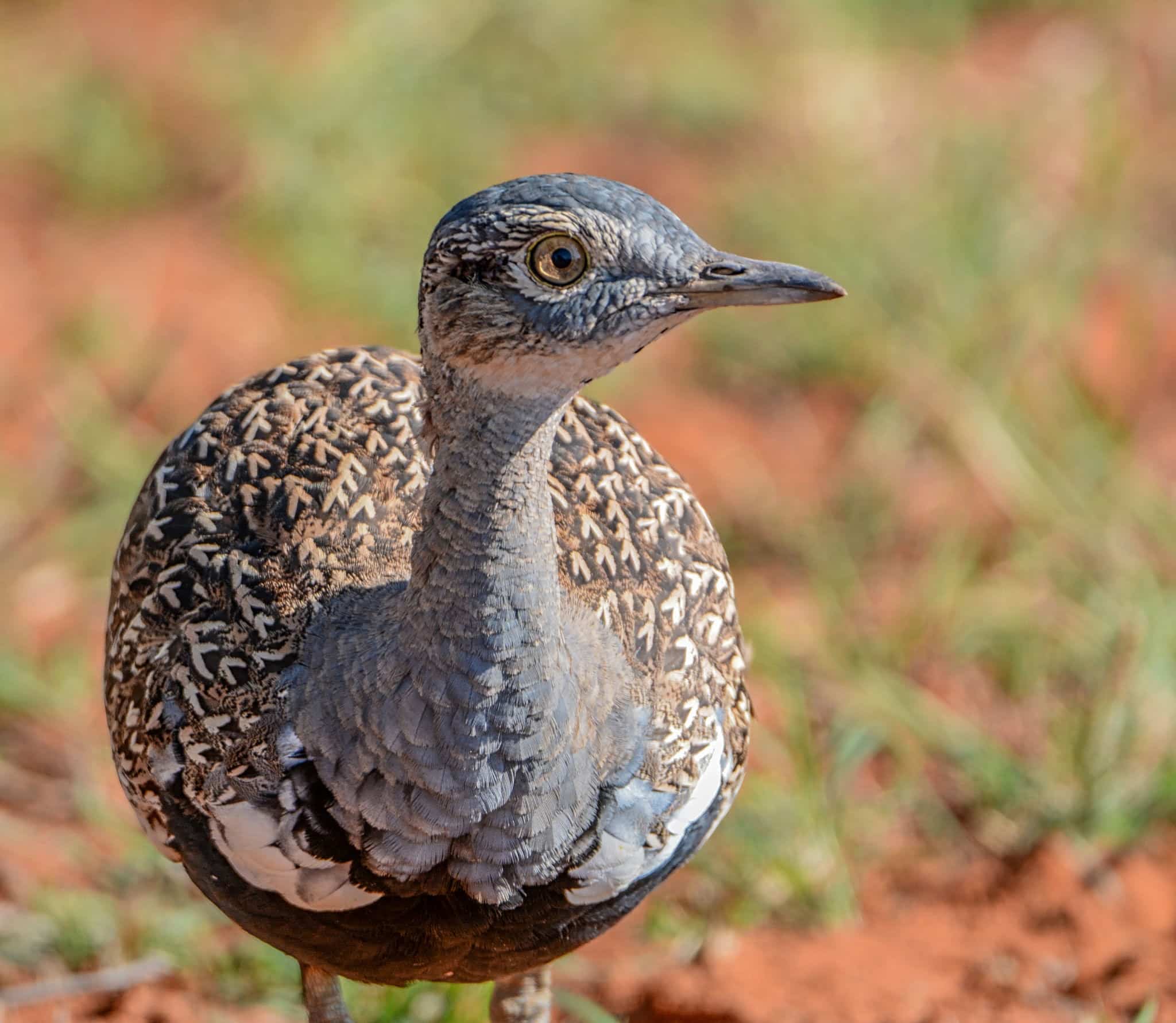
29. Korhaan
Place of Origin: Africa
Regions of Habitat: Grasslands, savannas
Scientific Name: Eupodotis spp.
Korhaans are large, ground-dwelling birds native to Africa.
They are known for their distinctive booming calls during mating displays. These birds have long legs and strong feet adapted for running rather than flying.
The males often have striking plumage patterns to attract females.
Interesting Fact: Male korhaans have inflatable throat sacs that they use to produce booming calls during courtship.
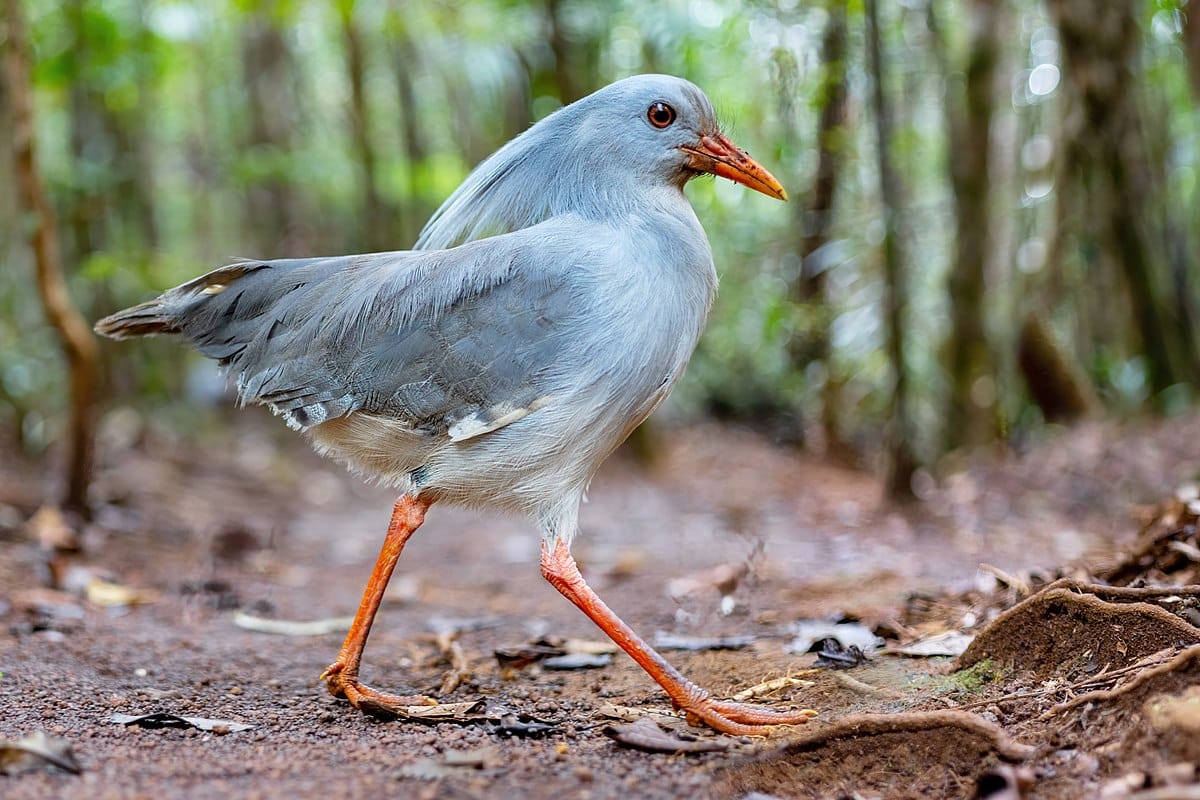
30. Kagu
Place of Origin: New Caledonia
Regions of Habitat: Forests
Scientific Name: Rhynochetos jubatus
Kagu is a unique bird native to New Caledonia, an island in the South Pacific.
It is known for its striking appearance, with slate-blue feathers, long legs, and an elegant crest.
The kagu is primarily a ground-dwelling bird, foraging for insects and small creatures in the forest.
Unfortunately, due to habitat loss and introduced predators, the kagu is considered endangered, making conservation efforts crucial for survival.
Interesting Fact: Kagus are flightless birds endemic to New Caledonia, making them vulnerable to habitat loss.
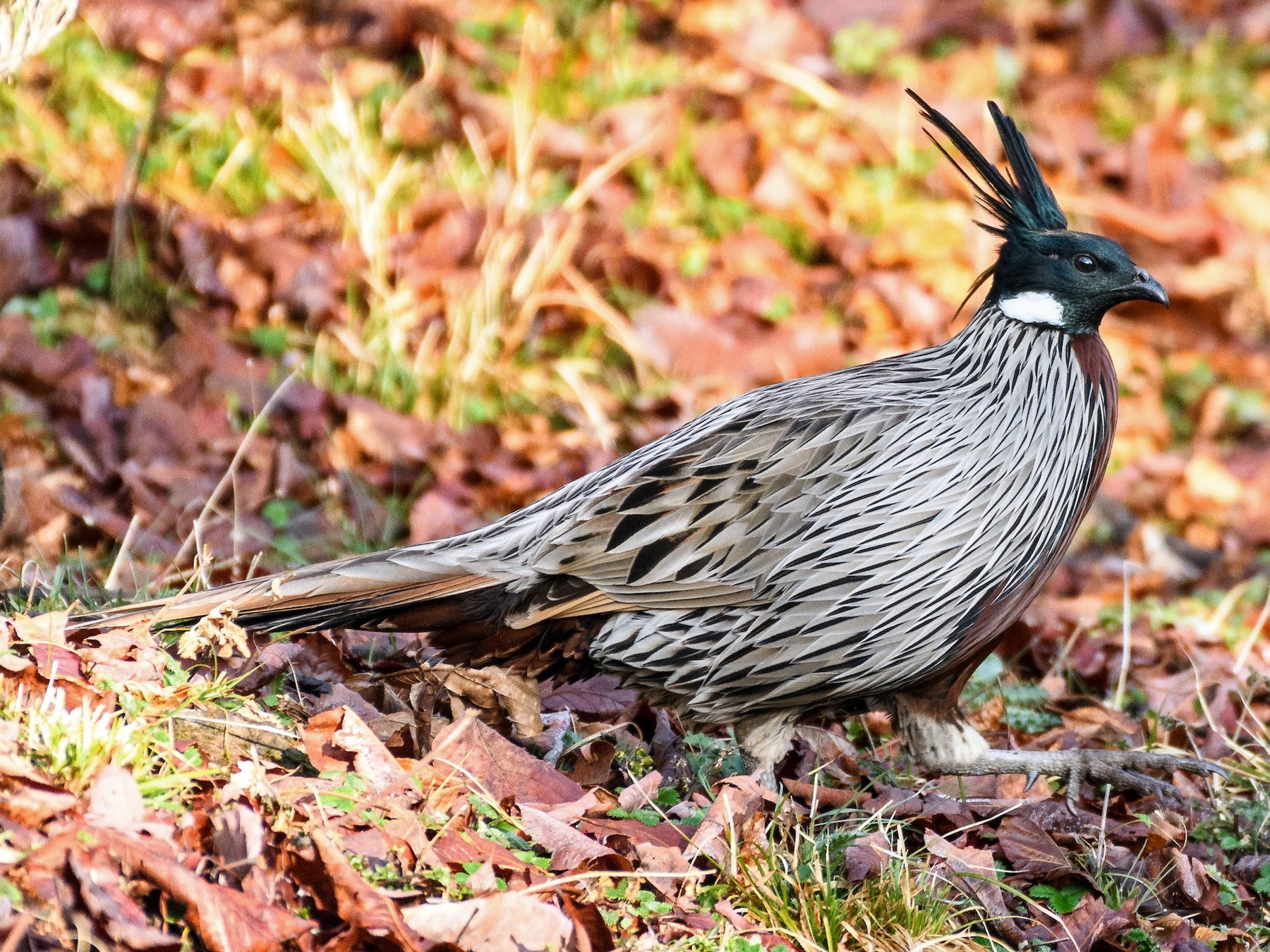
31. Koklass Pheasant
Place of Origin: Himalayas, Asia
Regions of Habitat: Forested mountains
Scientific Name: Pucrasia macrolopha
The Koklass Pheasant is a medium-sized bird native to the forests of the Himalayas and parts of Central Asia.
It is known for its striking plumage, with males featuring a distinctive blue-grey head and chestnut-brown body, while females exhibit more muted colors for camouflage.
Their diet primarily consists of seeds, berries, insects, and plant matter on the forest floor.
Due to habitat loss and hunting pressures, the Koklass Pheasant faces conservation concerns in some regions.
Interesting Fact: Koklass pheasants are monogamous and form strong pair bonds, often remaining together for life.
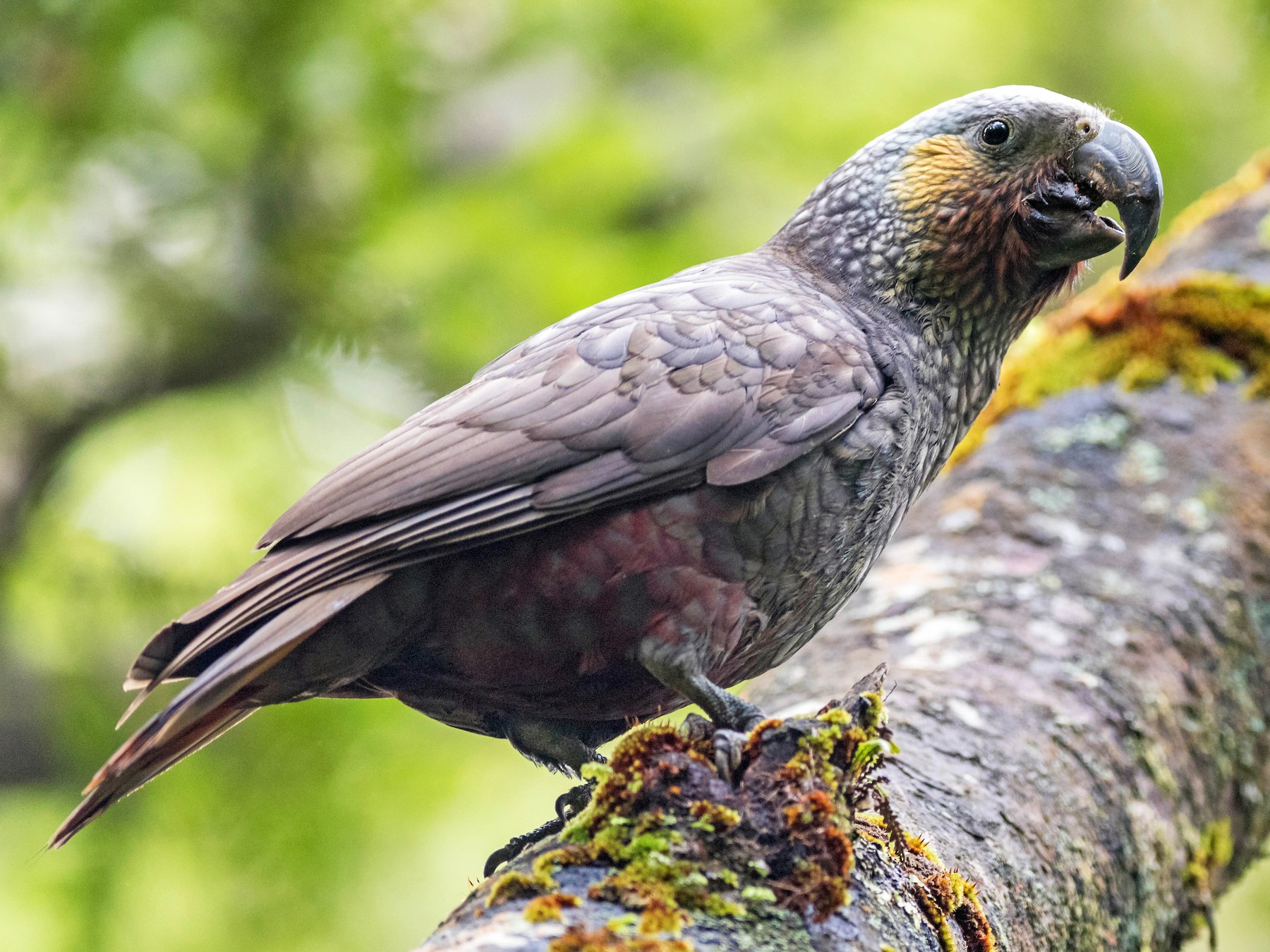
32. Kaka
Place of Origin: New Zealand
Regions of Habitat: Forests
Scientific Name: Nestor meridionalis
Kakapos, also known as “kaka,” are native parrots of New Zealand. They are known for their vibrant green plumage and distinctively long, curved beaks.
Unlike many parrots, kakapos are flightless, spending much time on the forest floor.
Unfortunately, they are critically endangered due to habitat loss and introduced predators.
Interesting Fact: Kaka parrots are excellent climbers, using their strong beaks and claws to grip tree trunks and branches.
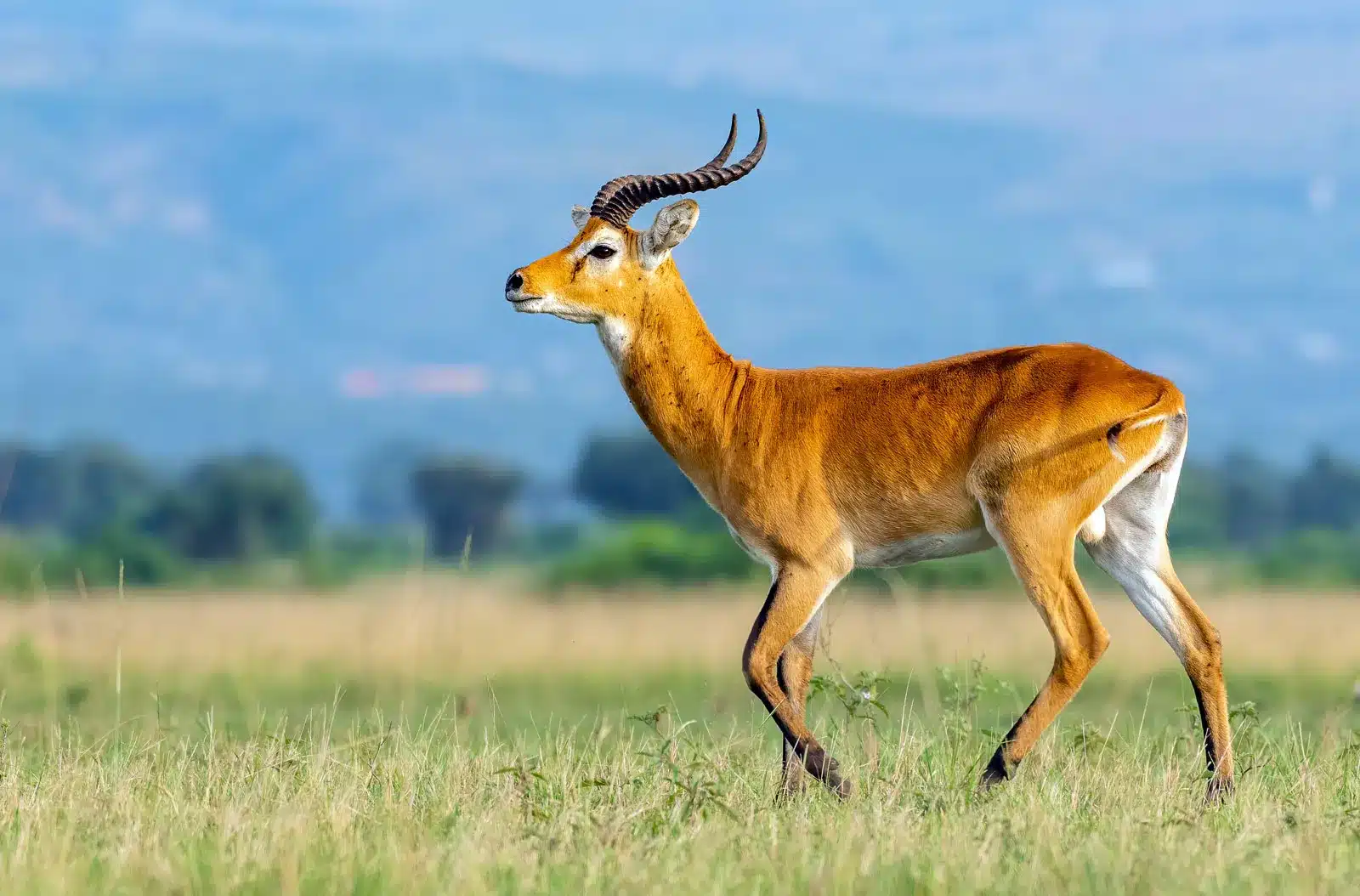
33. Kob
Place of Origin: Africa
Regions of Habitat: Grasslands, savannas
Scientific Name: Kobus kob
Kob is a term that refers to the kob antelope, native to Africa.
They are known for their reddish-brown coat and distinctive lyre-shaped horns in males. Kob are social animals, often forming large herds for protection.
Their habitat includes grassy savannahs and floodplains, where they graze on grass and shrubs.
Interesting Fact: Male kobs establish territories during the mating season and use visual and olfactory cues to communicate with rivals.
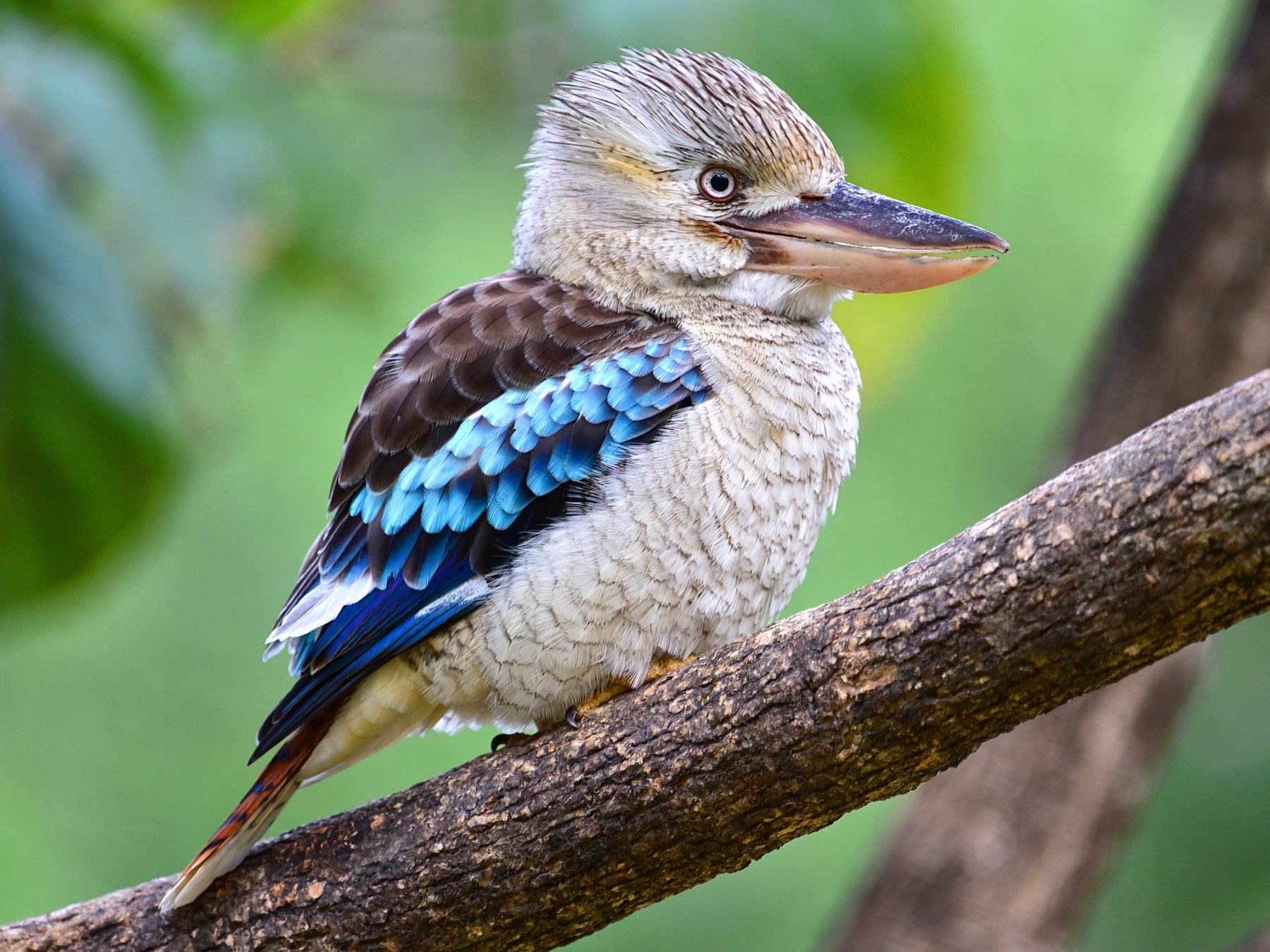
34. Kookaburra
Place of Origin: Australia
Regions of Habitat: Eastern Australia, including Tasmania.
Scientific Name: Dacelo novaeguineae
The Kookaburra is a large bird species known for its distinctive call, often described as echoing human laughter.
These predatory birds feed on insects, small reptiles, and other birds. They are a popular symbol of the Australian outback with a striking appearance marked by a large head and a stout bill.
Their robust beak aids in capturing prey, while their keen eyesight ensures they spot potential meals from a distance.
Interesting Fact: Kookaburras are not only known for their laughter-like calls but are also territorial birds. They often establish dominance over their territory, and their call warns other birds to stay away.
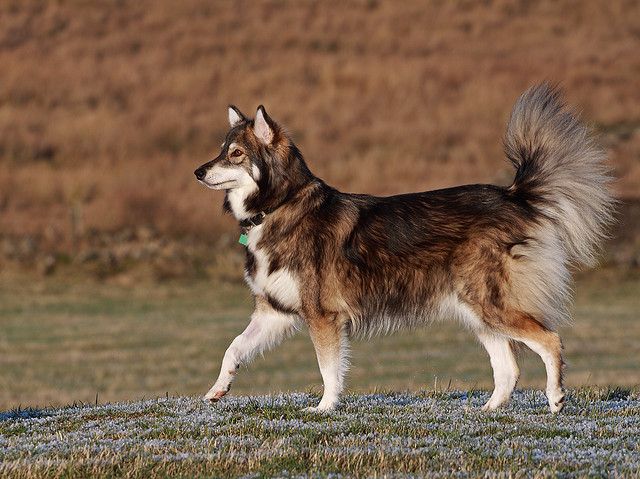
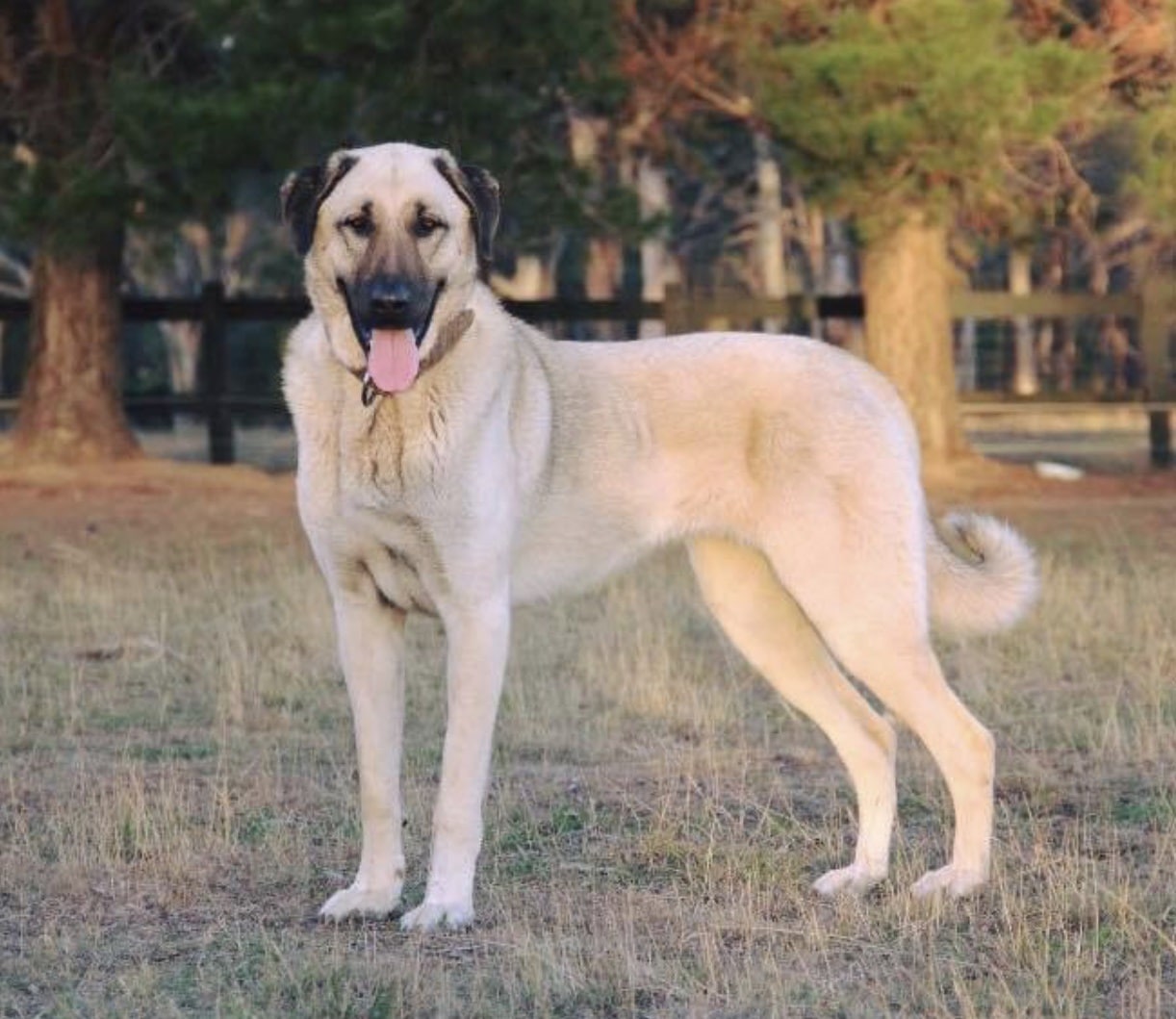
35. Kangal
Place of Origin: Turkey
Regions of Habitat: Sivas Province and neighboring areas in Turkey.
Scientific Name: Canis lupus familiaris (domestic dog)
The Kangal is a breed of livestock guardian dog originating from Turkey.
Recognized for its loyalty and protective nature, this breed is adept at guarding livestock, especially sheep, from predators like wolves and bears.
Physically, Kangals possess a muscular build, a dense double coat, and a distinctive black mask around their eyes.
Interesting Fact: The Kangal dog has been declared a national treasure in Turkey. For centuries, their protective instincts and unwavering loyalty have made them invaluable to Turkish shepherds.
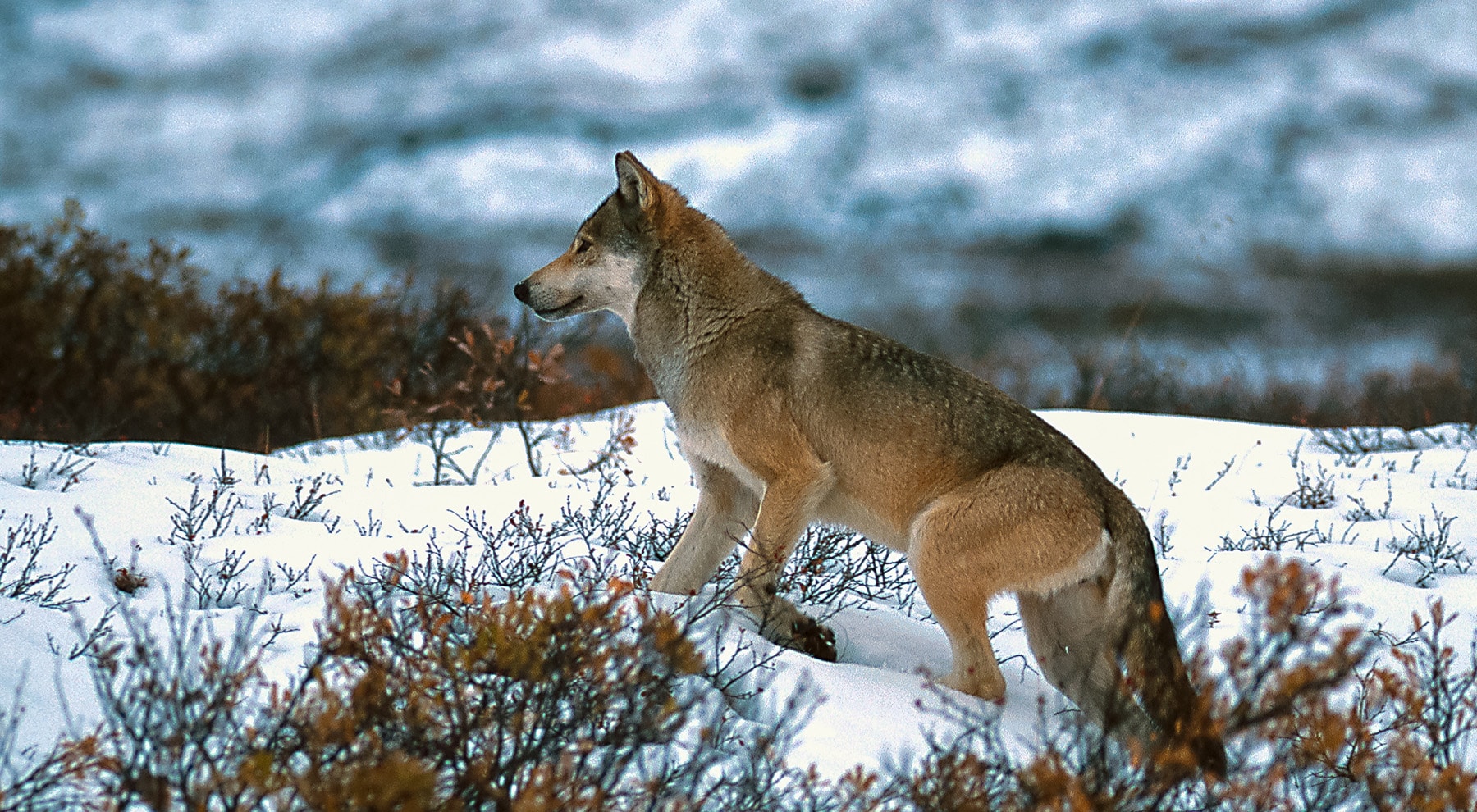
36. Kenai Peninsula Wolf
Place of Origin: Alaska, USA
Regions of Habitat: Kenai Peninsula in Alaska.
Scientific Name: Canis lupus alces
The Kenai Peninsula wolf is a subspecies of the gray wolf found exclusively on the Kenai Peninsula in Alaska.
They exhibit the typical behaviors and characteristics of wolves, including pack hunting and territorial behaviors.
Their diet primarily consists of small mammals, deer, and sometimes larger prey such as moose.
Interesting Fact: The Kenai Peninsula wolf’s isolation on the peninsula has led to unique genetic adaptations. Their distinct behaviors and characteristics make them a subject of interest for conservationists and researchers.
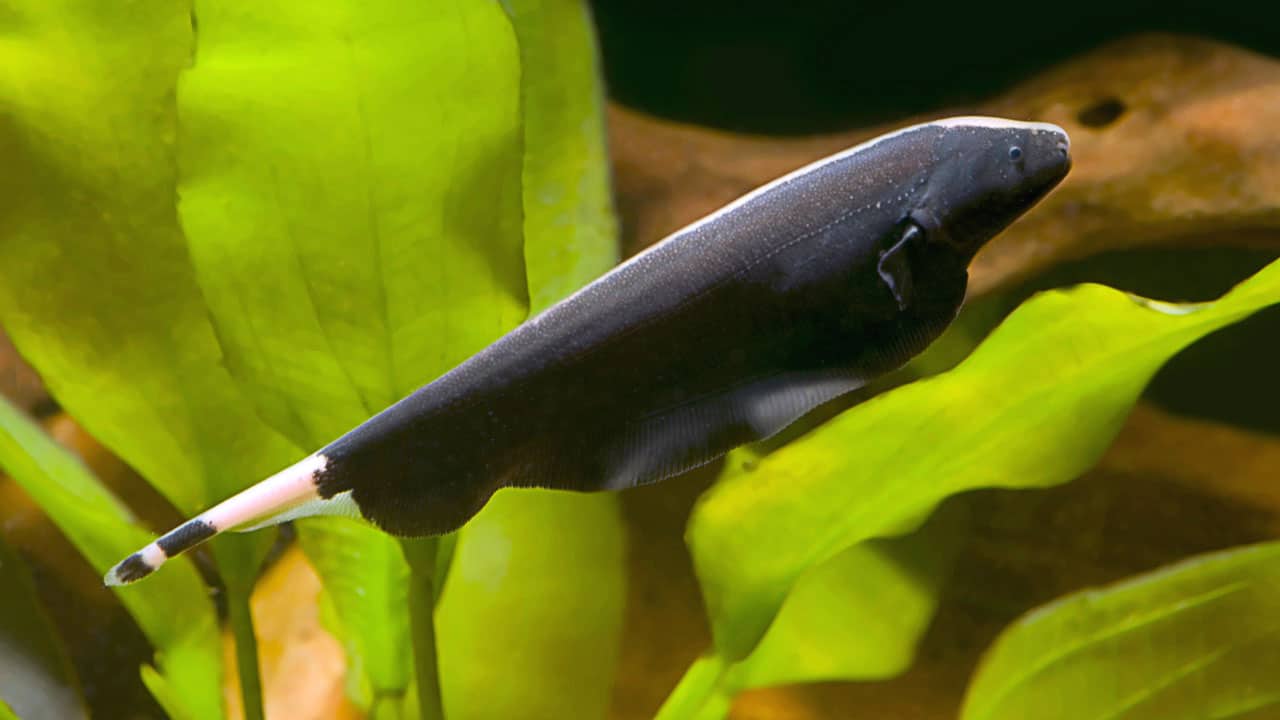
37. Knifefish
Place of Origin: South America, Africa, and parts of Asia.
Regions of Habitat: Freshwater rivers and streams.
Scientific Name: Gymnotiformes (order)
Knifefish, also known as electric fish, are a diverse group of fish known for their ability to produce electric fields.
These fish use electric fields for navigation, communication, and hunting. They possess elongated bodies and lack dorsal fins.
The electric discharge is produced by specialized cells called electrolytes in their tails.
Interesting Fact: The electric field produced by some knifefish species is so strong that it can stun or kill prey, making them efficient hunters in murky waters.
38. Kulinda Dog
Place of Origin: Siberia, Russia
Regions of Habitat: Siberian taiga.
Scientific Name: Canis lupus familiaris (domestic dog)
The Kulinda dog is a rare and ancient breed from the Siberian taiga.
They are believed to be one of the oldest breeds of sled dogs, renowned for their endurance and ability to thrive in harsh, cold climates.
Physically, they possess a thick double coat, erect ears, and a bushy tail.
Interesting Fact: The Kulinda dog’s unique genetics and adaptations to the cold Siberian environment make them invaluable to local communities for transportation and companionship.
39. Kakamega Forest Shrew
Place of Origin: Kakamega Forest, Kenya
Regions of Habitat: Kakamega Forest and surrounding areas.
Scientific Name: Myosorex varius
The Kakamega Forest Shrew is a small mammal species endemic to the Kakamega Forest in Kenya.
These shrews have a slender body, long snout, and a short tail.
They primarily feed on insects and small invertebrates found within the forest floor.
Interesting Fact: Due to the fragmented nature of their habitat and human activities, the Kakamega Forest Shrew is considered vulnerable. Conservation efforts are underway to protect this unique species.
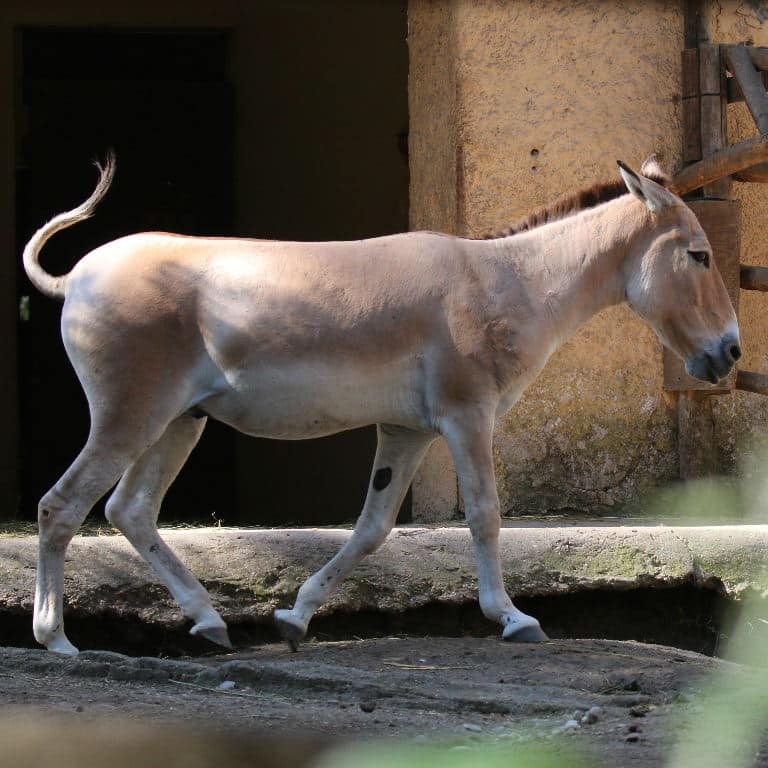
40. Khulan (Wild Asian Ass)
Place of Origin: Central Asia
Regions of Habitat: Steppes and deserts of Central Asia.
Scientific Name: Equus hemionus
The Khulan, also known as the Wild Asian Ass, is a species of wild equid native to Central Asia.
They resemble a small horse with a sandy-brown coat, short mane, and long ears.
Khulans are herbivorous, feeding on grasses and shrubs in their arid habitats.
Interesting Fact: The Khulan are known for their remarkable ability to survive in harsh desert environments, where they can go for long periods without water, obtaining moisture from their food.
Final Thoughts
Each animal, from Kangaroo to Khulan, has shown us the world’s diversity. As parents, we know how important it is to nurture our children’s curiosity about animals.
So, perhaps schedule a visit to the local zoo to see some of these animals up close or a nature hike to explore the habitats they call home.
Whatever you choose, keep encouraging your kids to ask questions, make observations, and share their experiences with others.
Comment below; which animal intrigued you the most? We are waiting to hear from you.





















































 9. Toca Lab: Elements
9. Toca Lab: Elements








































































































































