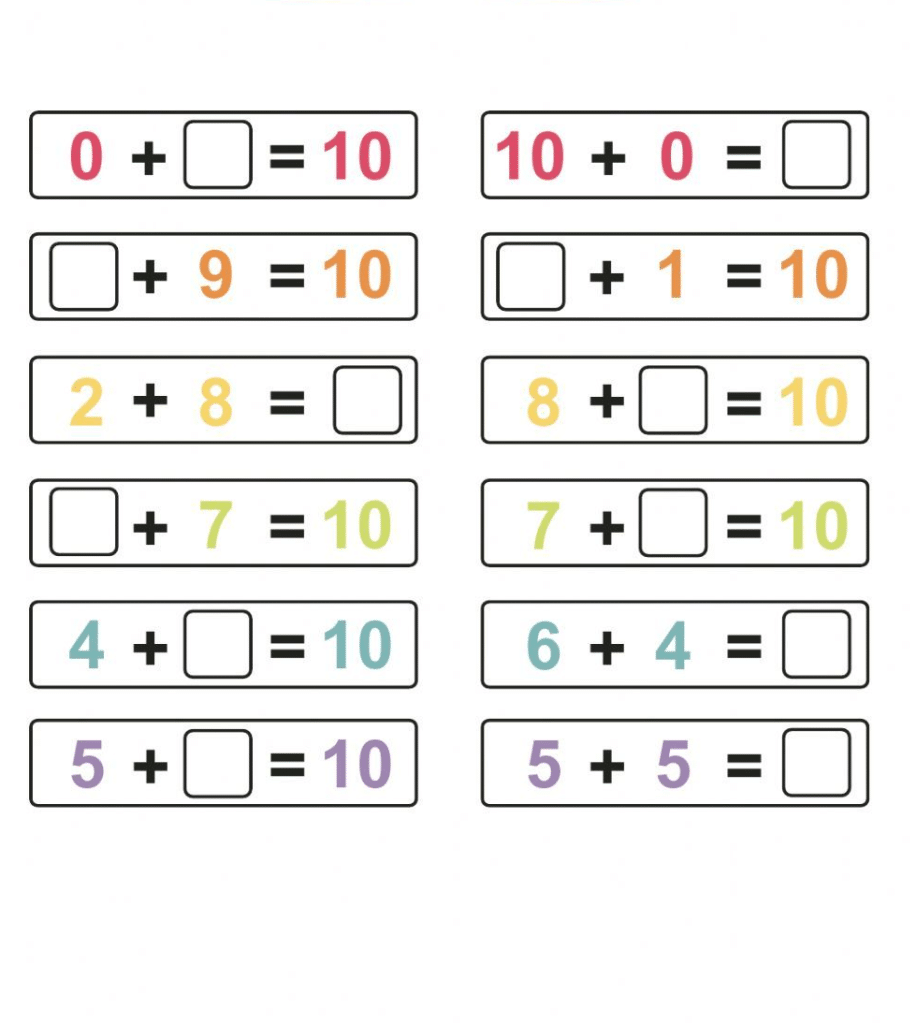
Are you on the lookout for some awesome and absolutely free educational websites to keep young learners engaged and excited? Well, you’re in for a treat! From thrilling interactive games to captivating lessons that make learning a blast, these websites are here to excite curiosity and inspire young minds.
Whether your child is a budding scientist, an aspiring artist, or a future math whiz, we’ve got something for everyone. Get ready to unlock a world of knowledge, creativity, and endless fun as we unveil the ultimate list of the 40 Best Free Educational Websites for Kids in 2023.
Let’s dive in and spark a love for learning that will last a lifetime!
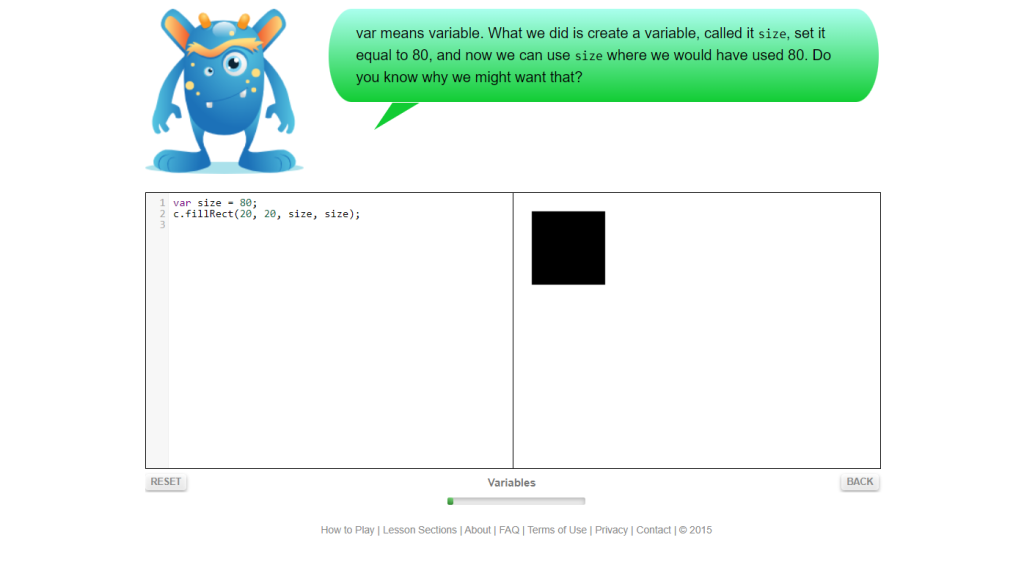
1. Code Monster
Do your children have a strong interest in app development? If so, a website like Code Monster can be incredibly beneficial. It offers a user-friendly platform for learning various coding languages. For instance, the website features two interactive boxes. One box is used for writing code, while the other box visually displays the outcome of that code in action. It’s a fantastic tool to nurture their coding skills in a fun and engaging way!
2. Plainmath
Plainmath is an incredible nonprofit math encyclopedia that students love. It’s a widely used platform that offers a treasure trove of unsolved math problems along with their solutions. What’s even more amazing is that anyone can join in and contribute to the platform, helping to enhance the learning experience for students. This collaborative effort ensures that students grasp concepts perfectly and have the resources they need at their fingertips.
3. Brighterly
Experience the brilliance of Brighterly, an exceptional online platform revolutionizing math education. Its remarkable features and user-friendly design establish it as an invaluable resource for both kids and students seeking to master math challenges. Say goodbye to boring math lessons and hello to an exciting world of interactive learning. Brighterly is your gateway to engaging math exploration, making concepts come to life in an enjoyable and captivating way. Elevate your math journey with Brighterly and embark on a path of effortless comprehension and joyful discovery.
4. Sesame Street
Sesame Street offers an enchanting website that will captivate your children with its engaging design. Through a variety of videos and games, kids can embark on an educational adventure to explore animal sounds, letters, colors, rhymes, and so much more. This platform provides a delightful and interactive way for children to expand their knowledge while having loads of fun. Join your little ones on a journey of discovery with Sesame Street, where learning and play come together in the most delightful and enriching way.
5. Multiplication Games
Fostering knowledge is crucial for young minds aspiring towards a tech-savvy future. When it comes to nurturing a strong foundation in mathematics, there’s no better destination. Unlocking the world of decimals and embracing the fun of Multiplication Games, this platform stands as an ideal learning hub for kids across all age groups. Set your children on a path of enhancing their technological skills with a solid educational base right here.
6. National Geographic Kids
National Geographic Kids presents an ideal online space for young learners to immerse themselves in the captivating realm of animals. Here, kids can explore the facts of nature. With National Geographic Kids, the journey of discovery unfolds, allowing your kids to develop a deep appreciation for the natural world while having a blast along the way.
7. Star Fall
Since its establishment in 2002, Star Fall has been a renowned educational website catering to kids worldwide. Beyond captivating comics, the platform offers a rich array of nonfiction books, plays, and more. With its global audience in mind, Star Fall provides a delightful blend of learning and enjoyment for children. Engage your kids in a world where fun seamlessly blends with education as they embark on a journey of discovery and enrichment through the dynamic offerings of Star Fall.
8. Swift Playgrounds
Swift Playgrounds emerges as an innovative creation from Apple, designed to introduce kids to the world of coding effortlessly. This platform serves as a captivating gateway, making coding an enjoyable and engaging experience. Through interactive puzzles, students enjoy an interesting journey to master the Apple programming language, fostering both logical thinking and creativity. Swift Playgrounds not only equips young minds with valuable coding skills but also infuses the learning process with excitement, offering a dynamic space where knowledge and play converge seamlessly.
9. How Stuff Works
Discover a treasure of answers to your kid’s curious questions about How Stuff Works. Whether they wonder about the uniqueness of time zones across countries or the causes of rainfall, this website holds the keys to knowledge. With an extensive collection of articles about technology, finance, culture, science, and entertainment, How Stuff Works offers an enriching experience for young minds seeking to discover the wonders of the world. Empower your child’s quest for understanding with this platform that nurtures curiosity and provides valuable insights into the workings of our fascinating universe.
10. Fun Brain
Step into the engaging realm of Fun Brain, a premier destination for exploration and growth. Catering to a wide range of grades from Pre-K to 8th grade, this platform boasts an array of activities tailored to each level. Immerse your child in a world of captivating games, enriching books, and insightful videos designed to foster academic development. True to its name, Fun Brain ingeniously weaves cognitive growth into an enjoyable journey, offering a seamless blend of education and entertainment. Elevate your child’s learning experience with this dynamic resource, where fun and knowledge harmoniously blend to nurture young minds.
11. Scholastic
Explore the wonders of Scholastic, an outstanding online learning hub tailored for kids. The platform presents a curated collection of activities thoughtfully organized by grade levels, extending from Pre-K and beyond. Children can craft their own comics, connect with peers, read captivating books, and engage in delightful games. Scholastic stands as a comprehensive online haven catering to a diverse range of educational pursuits. With its rich array of interactive experiences, Scholastic offers young learners a holistic platform where learning and fun blend seamlessly.
12. The Science Spot
Are you tasked with teaching science subjects and finding it challenging to determine the best lesson sequence? The complexity of organizing lessons might hinder your student’s understanding of the subject matter. Fear not, for The Science Spot comes to the rescue! This incredible website offers a solution by providing well-structured activities and lesson plans for various science topics. With The Science Spot as your guide, you can confidently navigate the teaching journey, ensuring your students grasp scientific concepts effectively and with ease. It empowers you to create a seamless and engaging learning experience for your students.
13. Gooru
Gooru stands as a remarkably valuable online platform designed with the sole purpose of empowering children to become adept learners at an accelerated pace. Its objective centers around the enhancement of individual learning experiences to create a new era of educational excellence. At the heart of Gooru’s mission lies a collection of state-of-the-art tools carefully curated to drive improvements in the learning process. With Gooru’s innovative approach, children are equipped with the means to unlock their full learning potential, paving the way for a brighter and more efficient educational journey.
14. Edutopia
Edutopia centers its primary attention on preparing students for academic growth and advancement. Undoubtedly, this website proves to be an invaluable resource for your child’s educational journey. Offering a plethora of enriching materials such as videos, informative posts, insightful articles, and beyond, Edutopia creates an immersive learning environment. With its diverse range of educational tools and content, Edutopia serves as a guiding light, illuminating the path toward enhanced academic excellence for students of all ages. Your child is certain to find a wealth of support and inspiration within the treasure of resources that Edutopia provides.
15. PE Central
PE Central emerges as a dedicated online hub designed to cater to the aspirations of physical education enthusiasts. Beyond benefiting children, this website extends its reach to educators, providing a valuable platform to enhance their teaching skills through the array of materials it offers. From comprehensive lesson plans to innovative assessment ideas, PE Central equips teachers with a wealth of resources to elevate their knowledge.
16. DIY
Welcome to DIY, a vibrant community where kids can explore and acquire exciting new skills. If your child is eager to embark on thrilling ventures, DIY is the perfect destination. With an extensive library of thousands of projects complemented by instructional videos, this platform fuels curiosity and creativity. The best part is the available free trial, enabling your child to sample and experiment with abundant resources. From crafting to coding, DIY offers a world of opportunities for young learners to discover their passions and unleash their potential.
17. Science Bob
If you’re on the lookout for a perfect platform to introduce your child to the wonders of science, look no further. Science Bob has you covered, making the process seamless and enjoyable. This website stands as a premier choice for young minds venturing into the realm of science. From research to Q&A and engaging experiments, Science Bob offers a diverse range of sections that cater to different activities. With its user-friendly interface and captivating content, Science Bob creates a valuable and accessible space for kids to dive into the captivating world of science exploration and discovery.
18. BBC History
Start on an exciting online journey with this adventure-packed website, crafted to offer kids a delightful blend of exploration and learning. Engaging quizzes, captivating games, and an array of activities await, ensuring children stay happily occupied. Beyond the acquisition of knowledge, this platform seamlessly integrates education and entertainment, ensuring a joyous learning experience. It’s a dynamic learning destination where young minds delve into diverse cultures and ancient customs of other nations, fostering a global perspective.
19. Highlights for Kids
For an enduring source of entertainment and education, Highlights for Kids is a timeless website. Here, children can unleash their creativity, indulge in reading, and engage in playful activities. The site offers a plethora of captivating features, including art projects, interactive science experiments, animated tales, and an array of games that invite exploration. The animated stories, in particular, hold a magnetic charm, captivating young minds and keeping them engrossed. With Highlights for Kids, your children will find a captivating haven that seamlessly blends learning and amusement, making every moment spent on the site an enriching and delightful experience.
20. Learning Games for Kids
Encourage your child’s creativity through the power of games! Look no further than the Learning Games for Kids website, where a diverse array of engaging games awaits. This dynamic platform offers a wealth of options spanning multiple subjects, including science, spelling, literature, vocabulary, brain challenges, social studies, and even artistic pursuits. With a treasure trove of options at their fingertips, your child can immerse themselves in a world of enjoyable learning. Learning Games for Kids is your go-to destination for sparking enthusiasm and enhancing knowledge in an interactive and entertaining manner, making education an exciting adventure for your young learner.
21. Scratch
Introducing Scratch, a specialized online platform tailored for children aged 8 to 16. It’s a digital playground where young minds can nurture their programming skills without the need for traditional coding. Here, the magic happens through assembling colorful “scratch blocks,” eliminating the complexities of writing intricate code. This innovative approach empowers kids to unleash their creativity and construct an unlimited imaginative project. From interactive stories to captivating animations, the possibilities are endless.
22. TedEd
Enter the world of TedEd, where simplicity meets profound impact. As a favored destination among children, this website’s concept is elegantly straightforward yet incredibly influential. TedEd transforms young minds into global thought leaders, offering a platform to share unique ideas that can resonate across the world, enriching the lives of others. It’s a virtual platform for innovation where your child’s imagination takes flight and contributes to collective knowledge. Moreover, TedEd offers a diverse range of resources tailored to various grade levels, ensuring a seamless learning experience that caters to every young learner’s needs.
23. Disney Jr.
For young fans of Mickey and Friends, Disney Jr. offers an amazing world that’s bound to capture their hearts. Dive into a world where learning is seamlessly blended with beloved characters. Through engaging videos, children look up to cognitive growth, enhancing skills like color matching, hand-eye coordination, and memory development. Disney Jr. is more than entertainment- it’s a gateway to fostering essential abilities in a playful and captivating manner. Watch as your child’s favorite characters become guides on an educational adventure, making learning both enjoyable and enriching.
24. Time for Kids
Step into the world of Time for Kids, a dynamic news website tailor-made for young readers. This platform offers an array of news stories carefully curated to match different age levels and subjects of interest. By delivering age-appropriate content, Time for Kids aims to captivate young minds, fuel their empowerment, and ignite inspiration for their future endeavors. With a commitment to engaging storytelling, this website becomes a gateway to informed and curious young minds. Through Time for Kids, your children can explore the world and stay informed.
25. Grammar Bytes
If your child is struggling with grammar challenges, look no further than this website for a solution. Here, a multitude of interactive activities await, designed to put students’ grammar skills to the test through engaging multiple-choice exercises. As a delightful incentive, students can earn whimsical virtual prizes, adding a touch of cheesy fun to the learning experience. With this user-friendly platform, tackling grammar becomes an enjoyable journey, ensuring accuracy while infusing an element of excitement.
26. Pixton
Cartoons hold a special place in kids’ hearts, yet the art of their creation often remains a mystery. Pixton changes the game by empowering your child to become a cartoon creator. With this platform, your kid can craft and store their own cartoons right on the website. Pixton offers a treasure of resources that stand out, including tools to enhance the visual appeal of the cartoons. Unlock your child’s artistic potential and watch their imagination come to life as they embark on a creative journey with Pixton, where storytelling and artistic expression seamlessly merge into a world of endless possibilities.
27. Geoguessr
Geoguessr is the ultimate platform to challenge and refine your child’s geography skills. Through engaging questions about the whereabouts of people, this site puts their geographical knowledge to the test. The daily challenges cater perfectly to every young explorer. Geoguessr introduces an innovative game that expands kids’ horizons and presents them with exciting challenges. Beyond the thrill, it’s an exceptional opportunity for them to broaden their understanding of various locations.
28. Exploratorium
Among the wide array of science websites tailored for kids, Exploratorium stands out, offering an abundance of captivating materials for young enthusiasts in both science and arts. This contemporary platform redefines the approach to learning science, infusing innovation into the educational process. With its modern twist, Exploratorium captures young minds, inviting them on an engaging journey of exploration and discovery. Your children are bound to be thrilled as it ignites their curiosity and drives a passion for the wonders of science and the arts.
29. iCivics
True to its name, this website is dedicated to the realm of civics education. The high-quality games offered here engage players in a meaningful way. Designed not only for kids and students but also for teachers, it serves as a comprehensive resource. The best part? It’s a free platform open for exploration by kids and young learners today. Embark on a journey of civic discovery and empowerment, as this website equips the next generation with the knowledge and enthusiasm to shape their world.
30. Math is Fun
Math is Fun website is widely recognized as a comprehensive math dictionary. Filled with math-related resources, it caters to both teachers and kids, making it a captivating platform. What sets it apart is its ability to simplify intricate concepts through its dictionary feature, rendering even the most challenging topics easily understandable. This resource-rich website is an invaluable tool, fostering a deeper understanding of math for both educators and young learners.
31. StoryboardThat
Enter the realm of StoryboardThat, where your kids can effortlessly craft storyboards without the need for any specialized knowledge or skills. This user-friendly platform holds the key to unlocking the art of visual communication for young minds. Empowering children to convey their ideas through storyboards creatively, StoryboardThat serves as a valuable tool in nurturing their visual storytelling abilities. From imaginative narratives to educational projects, this website offers a seamless and accessible pathway for kids to explore the world of visual expression.
32. Numberphile
For kids struggling with math challenges, Numberphile is the perfect remedy. This innovative website is tailor-made to nurture and enhance math abilities in a creative and engaging manner. Complex math concepts become approachable and easily solvable, empowering your child to beat difficulties with confidence. The best part? Learning becomes a joyful adventure. Numberphile seamlessly blends education and entertainment, offering a delightful experience for little learners.
33. Science Made Simple
Explore an interesting website that introduces your kids to the captivating world of science. Science Made Simple serves as a gateway to uncovering fundamental facts about various science topics, experiments, and engaging projects. This platform is an invaluable resource that sparks curiosity and provides insights into the wonders of science. Through Science Made Simple, children are empowered to nurture their science potential from an early age.
34. Classics for Kids
Delve into the captivating world of music with Classics for Kids, a website dedicated to enhancing your child’s musical understanding. From unraveling musical terminologies to exploring the legacies of renowned composers, this platform provides a comprehensive resource for all things music-related. Not only is Classics for Kids a valuable learning hub for kids, but it also proves to be an amazing tool for music educators. By bridging the gap between theory and practice, this website empowers both young learners and teachers to dive deeper into the world of music.
35. KidsHealth
Introduce your children to the realm of hygiene and health through this insightful website. Here, they embark on a journey of discovery, unleashing facts about their bodies and overall well-being. A treasure of articles awaits, diving into various health-related topics tailored for kids. From decoding puberty to uncovering the secrets of the lungs and the brain, this platform equips young minds with valuable knowledge in an engaging and accessible manner. By embracing this resource, you empower your children with a deeper understanding of their bodies and health.
36. Homeschool.com
Homeschool stands as a beacon of assurance, offering a wealth of top-tier resources to guide you on this educational journey. This website serves as an enlightening hub, providing comprehensive insights into the world of homeschooling. Immerse yourself in a plethora of high-quality articles designed to equip you with knowledge and confidence. As an added bonus, Homeschool extends a helping hand with freebies that further enrich your understanding and approach.
37. Beestar
Discover Beestar, a dynamic platform where kids can put their math knowledge to the test through a range of engaging exercises and topics. Unlock the opportunity to register your child for exciting competitions against peers, adding an element of friendly challenge to their learning experience. The cherry on the cake is that Beestar offers a free account, allowing your child to explore and sample the wealth of educational offerings available on the website.
38. Education Week
Education Week stands as a dedicated news website tailored for young readers. Every week, it delivers newspapers filled with insightful content focused on educational topics. The best part? Access to this informative platform is entirely free. By engaging with Education Week, your kids gain a window into the world, staying informed about global happenings. Empower your young learners to broaden their horizons and stay connected with current events through this accessible and enriching resource.
39. Tate Kids
Tate Kids opens the door to a world of popular artworks, making art exploration effortless and engaging for kids. This website offers an array of interactive games centered around the realm of art. Additionally, quizzes are available to spark creativity and artistic thinking in your child. With an innovative approach that seamlessly merges education and entertainment, this platform paves the way for your child to appreciate, learn, and express themselves through art.
40. NickJr
The NickJr site holds a unique power. Bursting with a magnitude of captivating videos, this platform is a treasure waiting to be explored by every young adventurer. The videos are carefully curated to captivate and engage, leaving your kids thoroughly entertained. With NickJr, your children’s imaginations take flight, and they discover what sparks their hidden talents.
Summing It Up
In the vast digital landscape, these 40 best free educational websites hold a unique treasure of knowledge waiting to be unlocked by young minds.
Whether your child is a budding scientist, an aspiring artist, a future mathematician, or simply curious about the world around them, these websites provide the tools and resources to inspire growth.
In the ever-evolving world of education, these websites serve as gateways to exploration, offering a world of information and insights at the click of a button.
By embracing these educational websites, we empower our kids to learn, explore, and thrive in a world that constantly demands knowledge.