Isn’t it surprising to think of an animal or mammal that gives eggs and milk?
There are two kinds of organisms: oviparous (the ones that lay eggs) and viviparous (the ones that give birth).
The concept of an organism capable of producing eggs and milk often surprises many.
This guide is designed to intrigue and educate, highlighting this unique mammal’s unique and enchanting characteristics.
While there are certain rules on reproduction, unique animal behaviors continue to defy them.
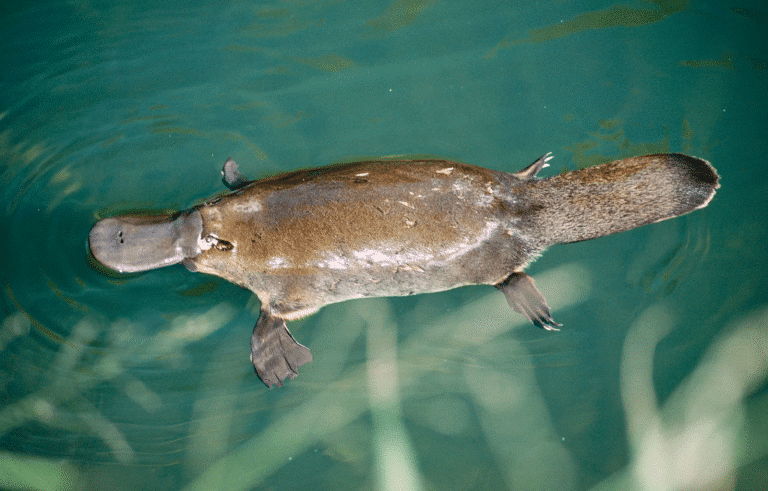
Thus, out of all the species on the planet, the platypus is a unique animal that lays eggs and gives milk.
If you’re curious about more intriguing creatures, check out our article on every fascinating ‘animal with f‘ to discover a world of diverse and astonishing wildlife.
For an enlightening exploration of such unique species, delve into our comprehensive guide.
In this article, we will take you through elaborating to make you understand its detailed anatomy.
What is Platypus?
A platypus is an animal with a flat beak that often resembles a duck’s. It is one of the fastest mammals and is an extremely good swimmer.
Contrary to dolphins, platypus is a very introverted mammal who is shy and calm.
It’s for their introverted nature that you may not often get to see platypus. They live on land and water.
These mammals are mostly found in Southern Australia and are considered one of Australia’s most ‘unique’ animals.
Since they can live on land, they share similar characteristics and features to various aquatic animals.
Why is Platypus Distinct as a Mammal?
The characteristic of laying eggs and giving milk is what sets platypus apart from other mammals.
The mammals are usually responsible for giving birth to their kids and feeding them milk.
On the other hand, amphibians who live in water or fly in air usually lay eggs.
In 1884, William Hay Cadwell, a Scottish scientist, discovered this unique characteristic of platypus to lay eggs.
The left ovary is important in determining the exact impact, especially in terms of evolution for birds and mammals.
A platypus has mammary glands, but there aren’t any teeth. As far as milk is concerned, it is usually released from the skin pores.
Once the egg hatches and a baby platypus is born, the milk starts secreting from the pores of the mother’s skin.
Initially, babies are born with teeth that eventually fall off as they grow.
Instead of teeth, a platypus develops horny plates, which help them chew and grind their food.
Habitat of a Platypus
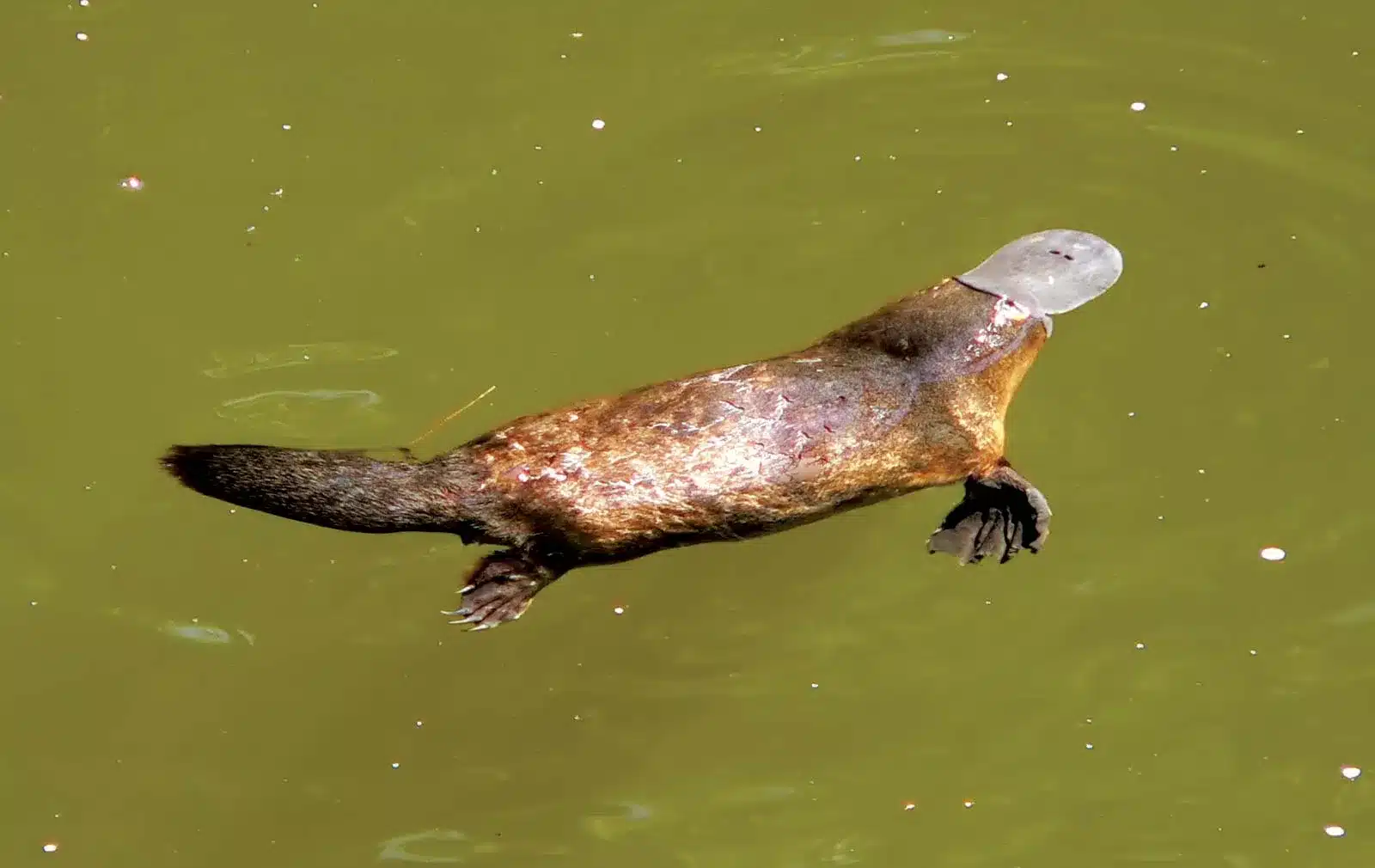
As stated above, platypus is an amphibian that can live on land and water.
Usually, platypuses live in freshwater systems across northern Queensland’s plateaus and tropical rainforest lowlands.
These platypuses are also found in the high altitudes of the Australian Alps or Tasmania.
Platypuses usually build on the banks of the river, where they spend most of their time when they are not foraging.
On the other hand, a lot of platypuses use stream debris as shelter.
Ideally, the most preferred habitat for a platypus is around the streak or rivers close to natural vegetation.
These amphibians usually live around areas that feature pool-riffle sequences.
Feeding Behavior of Platypus
The platypus’ feeding behavior is unique, too, for they consume mostly during the night. They feed upon the aquatic invertebrates.
On average, these animals forage for around 10-12 hours per day, and the distance they cover during this period completely depends on their strength and distribution.
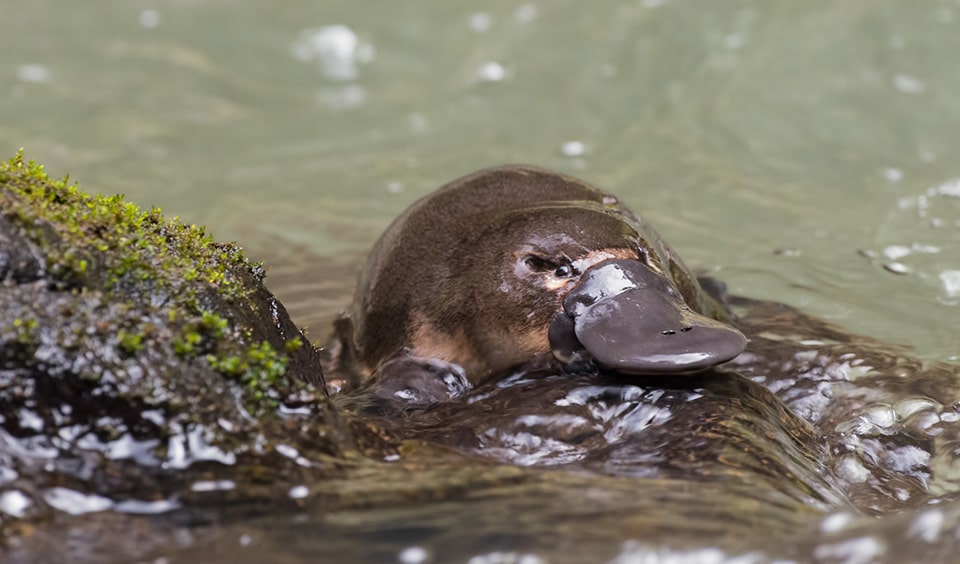
When a platypus is foraging underwater, they close their eyes, nostrils, and ears, and the bill remains their primary sense organ.
The bill has receptors sensitive to pressure and features electro-receptors, which it uses to detect its prey.
The bill acts as a small substrate for the prey, attracting them to the platypus. On a maximum basis, the platypus can stay underwater for 30-140 seconds.
During this period, they collect their prey aquatic invertebrates from the river bottom and hide them in their cheek pouches.
Afterward, they come to the water’s surface and float while eating the food they collected from the river bottom.
On average, the platypus usually prefers consuming benthic invertebrates like insect larvae.
The other organisms platypus consumes are water bugs, tadpoles, beetles, shrimps, freshwater pea mussels, and snails.
Platypus also catches moths and cicadas from water surfaces.
When they’re in captivity or breeding farms, platypuses are given freshwater crayfish or yabbies to eat.
Communication
Although platypuses are introverted and solitary animals, a group of them can live together in the same water body.
Currently, they communicate with each other because no vocalization is recorded.
However, those in captivity usually produce low-pitched growling sounds when the caretakers handle them.
Final Words
Studies have shown that the current-day platypus is more advanced than its predecessors.
It is small with functional teeth and widespread across a huge demographic.
Found mostly across Australia, platypus is capable of giving eggs and milk.
It is extremely common in Australia and features evolutionary limbs, so they should never be taken for granted.
Does the unique nature of the animal kingdom surprise you? Stay tuned with us to find much more interesting topics.