Lasers are high-energy beams of light that can cause eye and skin damage if safety is not observed. However, for some laser cutting enthusiasts and laser users, they often prefer to first build a manual work space at home. Therefore, while pursuing convenience, how to maximize the safety consideration of using a laser cutting machine at home is the focus of this article.
Getting to Know the Laser Classes
Differences in lasers, especially differences in safety, are defined by laser classes. Laser classification systems inform users of necessary safety measures and precautions, which help prevent accidents and ensure safety in places such as medical facilities and manufacturing plants.
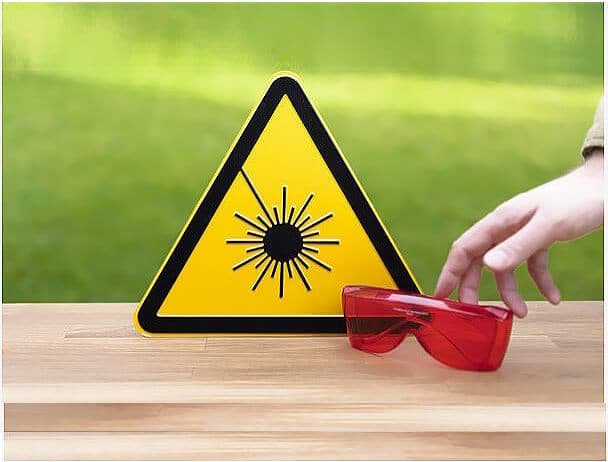

In addition to personal safety, laser classification increases responsibility and awareness of laser use. It helps create a safer environment and encourages responsible use of laser technology across all sectors.
Laser safety levels are classified based on the potential harm of lasers to human eyes and skin. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has developed a set of international standards (IEC 60825-1) to classify laser products into safety classes. Lower class lasers require basic precautions, while higher class lasers require strict controls and protective gear.
Class 1 Lasers
- Safest type of laser.
- Will not cause eye or skin damage even under normal use conditions.
- Examples include laser pointers, optical fiber communication, and laser barcode scanners.
1M Class Lasers
- Similar to Class 1 lasers, but can cause eye damage when viewed through optical instruments such as telescopes or microscopes.
- Examples include laser printers and laser CD players.
Class 2 Lasers
- Low-power lasers that can cause eye damage, but not skin damage.
- Usually visible and have relatively low power.
- Examples include laser pointers, laser projectors, and laser level instruments.
Class 3 Lasers
- Can cause eye damage and potentially cause skin damage under certain conditions.
- Usually visible and have higher power than Class 2 lasers.
- Examples include laser cutters and laser medical devices.
Class 3R: This is the less powerful subclass within Class 3. While eye injury is still possible, it’s less likely to occur from accidental exposure compared to Class 3B.
Class 3B: These lasers have higher power than 3R and pose a greater risk of eye damage, even with momentary glances.
Class 4 Lasers
- High-risk lasers that can cause serious eye and skin damage.
- Usually invisible and have very high power.
- Examples include laser weapons, scientific research, and industrial applications.
Tips for Safe Use at Home
Before You Cut:
- Safety First: Invest in proper safety gear. This includes laser-safety glasses with the appropriate wavelength rating for your cutter, respirator mask, and gloves.
- Know Your Machine: Read the user manual thoroughly. Understand emergency procedures, maintenance routines, and material compatibility.
- Workspace Preparation: Choose a well-ventilated area. Fumes and dust are common during cutting. Ideally, vent the fumes outside or use an air filtration system. Keep the workspace clean and clear of flammable materials.
- Material Matters: Not all materials are safe for laser cutting. Research to ensure the material won’t produce hazardous fumes or ignite. Avoid PVC, and halogenated plastics that release toxic gasses when cut.
When operating the laser cutter:
- Don’t Leave Unattended: Always monitor the home laser cutter while it’s in operation. Things can go wrong quickly, and supervision is crucial for fire safety. Unless you are using a Class I laser cutter machine, leaving the work area suddenly can be dangerous.
- Power Settings: Use the correct power settings for your material. Higher settings can damage the machine or cause scorching.
- Interlocks Engaged: Many laser cutters have interlocked safety covers. Never bypass these features; they prevent accidental exposure to the laser beam.
- Fire Safety: Keep a fire extinguisher readily available and know how to use it properly.
Additional Tips:
- Keeping Clean is Key: Regularly clean the laser cutter’s mirrors and lens to maintain optimal performance and safety.
- Be Wary of Reflections: The laser beam can reflect off shiny surfaces. Be mindful of beam paths to avoid accidental eye exposure.
- Maintenance Matters: Schedule regular maintenance for your laser cutter to ensure it’s functioning safely and efficiently.
Remember: Safe laser cutting practices require knowledge, preparation, and constant vigilance. If you’re unsure about any aspect of using your laser cutter, err on the side of caution and consult a professional or the manufacturer’s resources.
The Safest Laser Cutter for Home Use
Of course, you can also solve the problem from the source and find a laser cutter machine with strong safety performance, which can greatly reduce safety concerns.
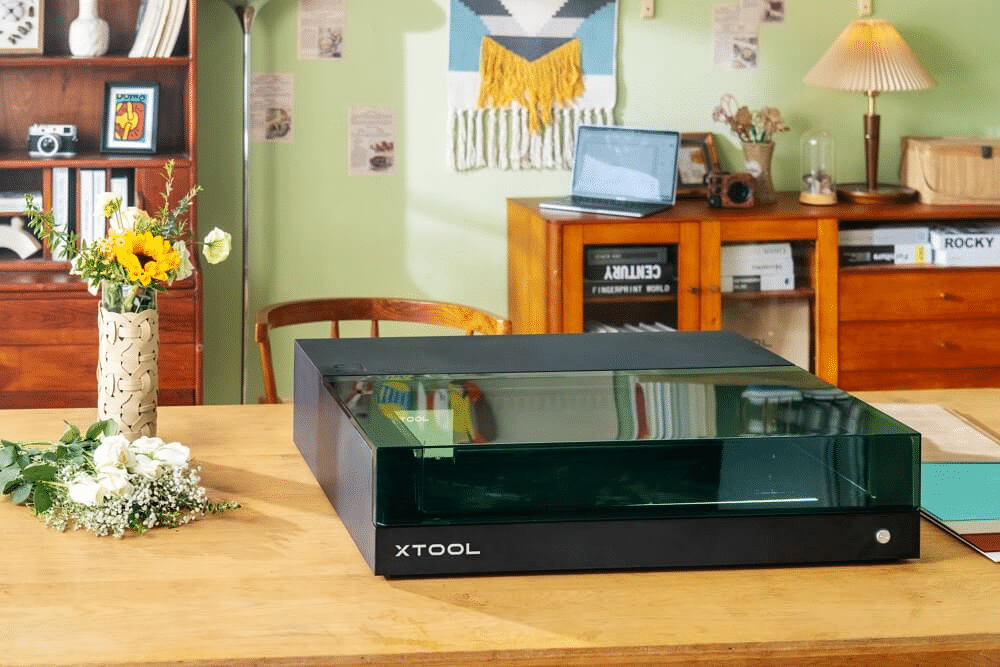
Class 1 laser cutters are distinguished by their inherent safety features and versatility, making them a safe and reliable option compared to open laser machines. The enclosed design of these engraving machines ensures that there is no risk of exposure to harmful laser radiation during normal use. It also prevents any potential fire hazard by confining the laser beam to a controlled environment.
xTool S1 is a class-one safety diode laser with 40W high-power. This enclosed machine integrates required safety features, such as dual laser filter covers, eliminating the need for safety glasses. Powerful functions, cutting efficiency, and safety are combined to increase user-friendliness. It is a safe and innovative laser machine that is suitable for anyone to use at home or in a small indoor studio.
Same as xTool S1, most first-class safety laser cutting machines are often equipped with automatic shut-off mechanisms. This mechanism is activated if someone opens the housing during operation, preventing any direct interaction between the user and the laser. It significantly improves user security. Some Class 1 laser products also have filter caps.
Conclusion
Overall, the safety of laser use is an important issue that users cannot afford to ignore. Understanding the establishment of laser classes, being aware of the safe use of laser machines, or shopping for safer laser products can help to achieve a safer use of laser cutters at home.