Approximately 2 million animal species in the world belong to the Kingdom Animalia.
These animals, in turn, belong to families based on their characteristics and similarities.
For instance, you can explore various families, such as those in our article on ‘animal with F,’ based on adaptability and sharing common traits.
Hereafter, families are further divided into smaller groups called genera and species.
The species are given two-word scientific names based on the Linnaean Taxonomy.
The Animal Kingdom classification is important to understand the families the animals belong to.
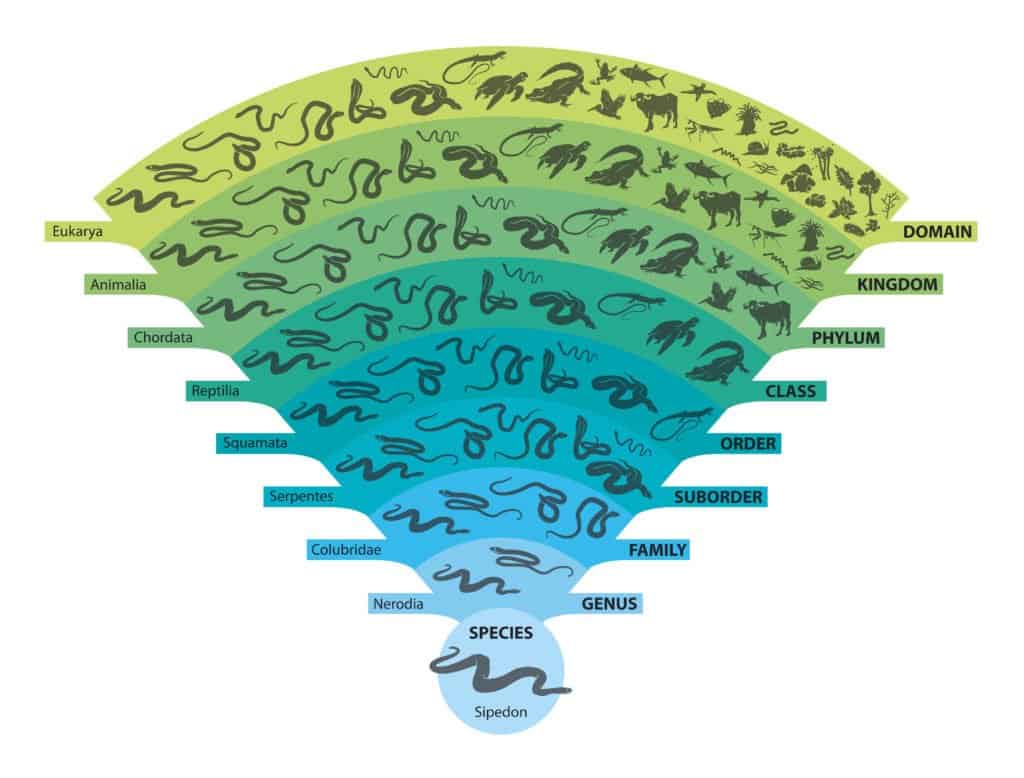
There are nine branches: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Suborder, Family, Genus, and Species.
So, without beating around much in detail, let’s dive deep into the Animalia kingdom and the wide world.
Animal Family Groups
Among the 5 animal kingdoms, namely, Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia, Kingdom Animalia is the largest kingdom, and the animals in this kingdom are divided into family groups.
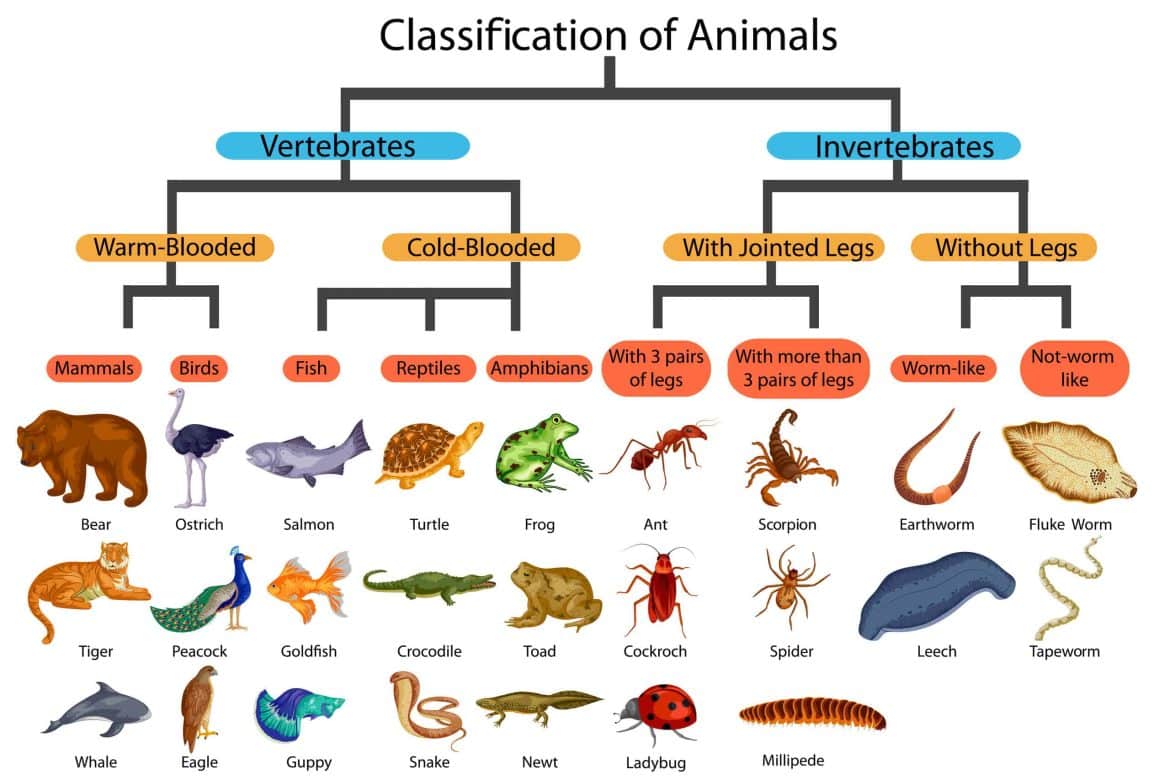
They are divided into Vertebrates (animals with a backbone) and invertebrates (animals without a backbone). The Vertebrates are further divided into different categories.
There are plenty of examples of vertebrates from the vast Animalia kingdom; the case of some is contained in our article on animal with ‘F’ that perfectly sheds light on our rich and diversified wildlife.
So, without any further ado, let us dive into the vast world of the kingdom and learn about their insight.
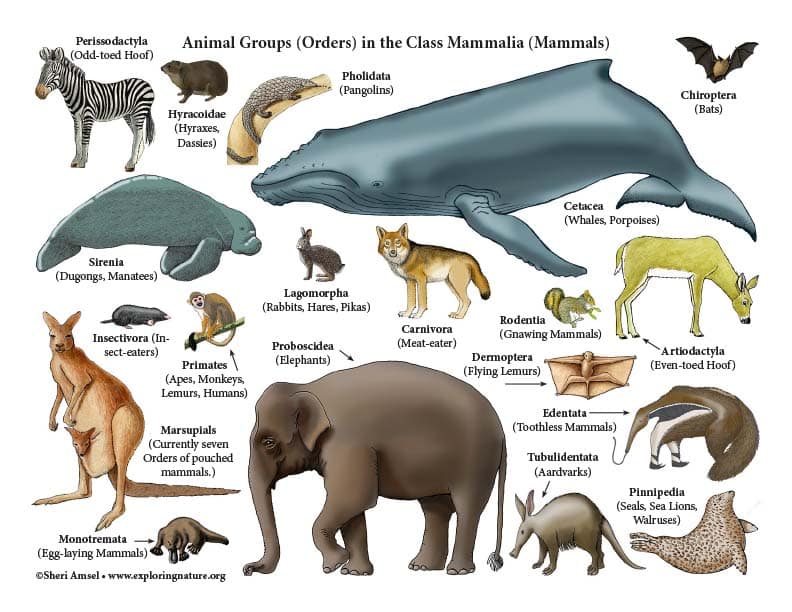
1. Mammals
Mammals are vertebrate animals that reproduce offspring and feed them through the mammary glands.
They are warm-blooded with hair on their body and have a backbone. Scientists have identified more than 6400 mammal species on Earth.
The order of mammals, by the number of species, are- Primates, Even-toed ungulates, and the Carnivora.
Humans fall under the primates, a group of mammals. For example, elephants, whales, Cows, etc.
2. Fish
Fishes are aquatic, gill-bearing animal families that lack limbs with digits. They live in water and have scales and fins on their body.
34,300 fish species have been discovered, exhibiting the greatest species diversity among vertebrates.
They are cold-blooded, and their body temperature varies according to the temperature changes.
Fishes are important resources for humans in the form of food, religious symbols, and pets.
Fishes are also caught for recreational activities and are kept at aquariums for exhibition. For Example- Black bullhead, Seal, etc.
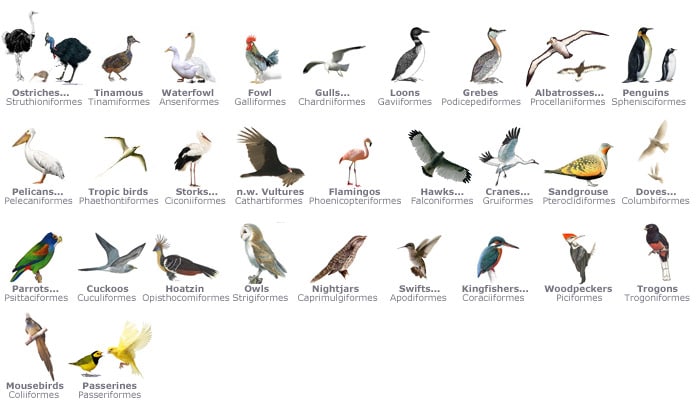
3. Birds
Birds are characterized by their feathers, toothless beaked jaws, four-chambered hearts, and strong yet lightweight skeletons to ease their flight in the open sky.
They have wings and lay hard-shelled eggs. They are found in sizes varying from 5.5 cm to 2.8m.
Apart from wings to fly, the birds have evolved for swimming, with their digestive and respiratory organs coordinating flight and swimming.
Birds are the only feathered theropod dinosaurs and are also considered reptiles in the modern cladistic sense. For example- Parrot, Owl, Falcon, Penguin, etc.
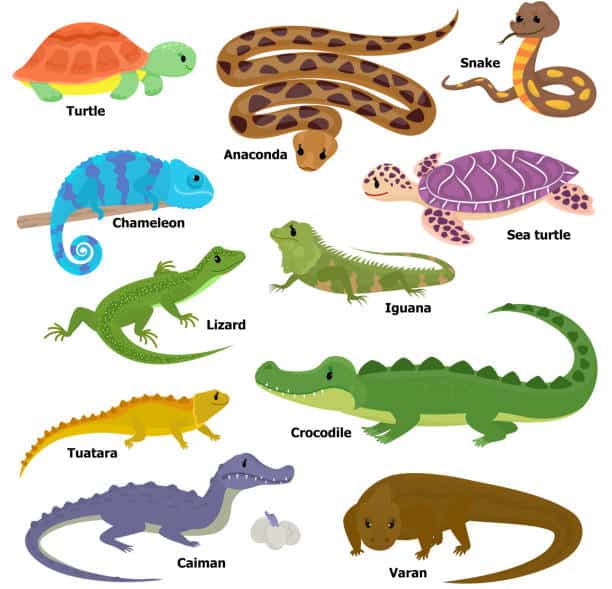
4. Reptile
Reptiles comprise the class Reptilia and consist of around 12,000 living species.
These are tetrapods(four limbs) and cold-blooded, with some being viviparous and others being oviparous.
Membranes for protection and transportation surround reptile eggs. They grow in sizes varying from 17 mm to 6 m, weighing more than 2200 lb.
They comprise four orders- Testudines or Turtles, Crocodilia or Crocodiles, Squamata or Lizards and Snakes, and Rhynchocephalia or Tuatara. For example, turtles, lizards, Chameleons, etc.
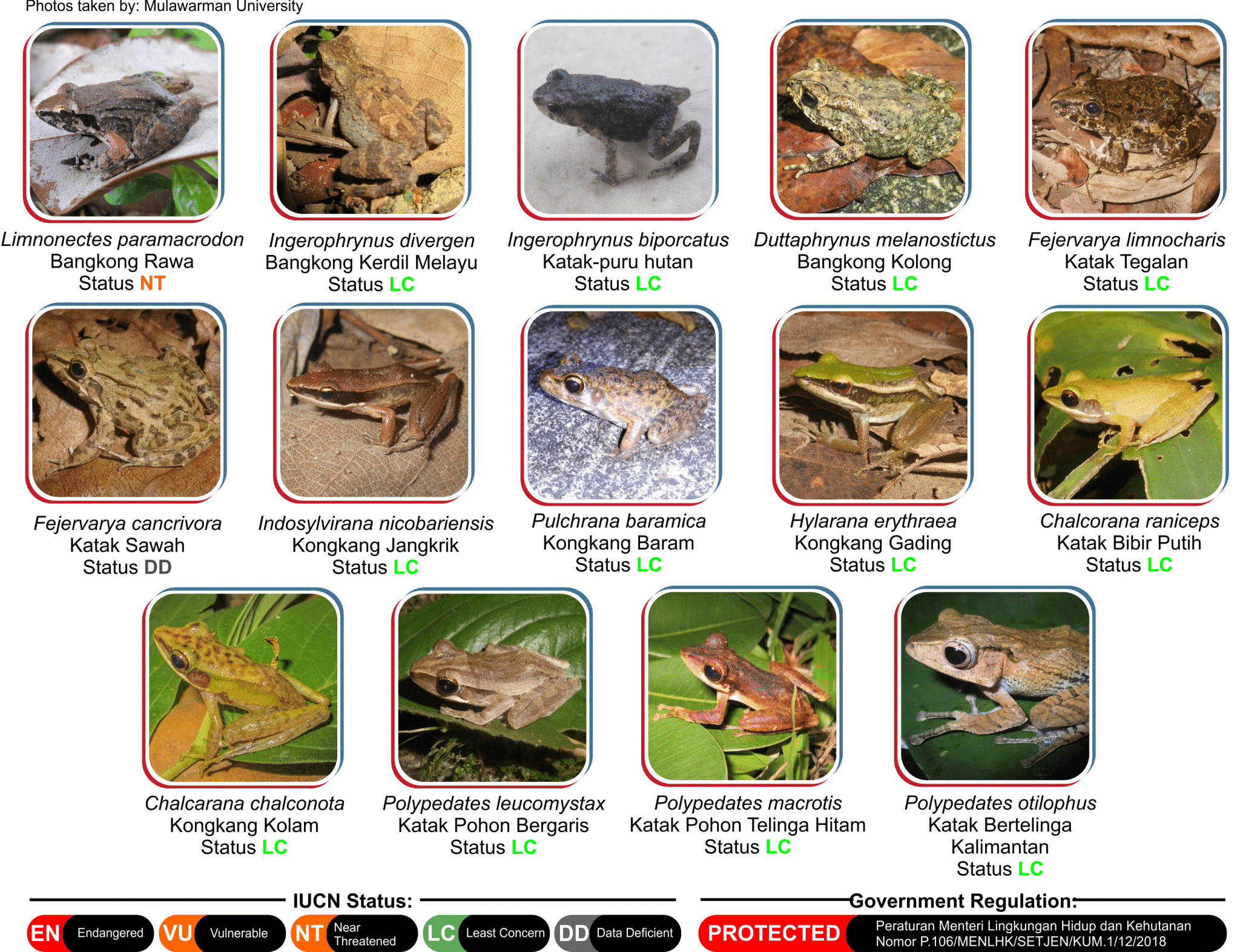
5. Amphibians
Amphibians are mostly semi-aquatic, with various habitats in freshwater, wetland, and terrestrial ecosystems.
These are anamniotic, four-limbed vertebrates that start their life mostly as aquatic larvae with gills and undergo metamorphosis to breathe with their lungs as adult amphibians.
They differ from reptiles since, unlike reptiles, they need water bodies to breed themselves.
They consist of three living orders- Anura or Frogs, Urodela or Salamanders, and Gymnophiona or Caecilians. For Example- Frog, Salamander, Diplocaulaus, etc.
Apart from the 5 families mentioned above, there are other families: Insects, Corals, Molluscs, Arachnids, and Crustaceans.
Insects have the most species in their family, with a more than 1.05 million count.
The taxonomists and scientists are working to discover more and acknowledge them in the various groups and families.
Conclusion
Even if over 2 million species of animals are accounted for in the given data above, it might be only 1% of the Earth.
There are innumerable undiscovered animals in the deep horizons of the layers of the Earth.
Animals form strong bonds among their families and with other families and friends, and we should all treat them with love and compassion.
While many animals have become extinct over time, many have evolved.
There are many more to discover and protect; we might get a whole new animal family.